- Ethiopian ATC on strike, no Notams, government hush up
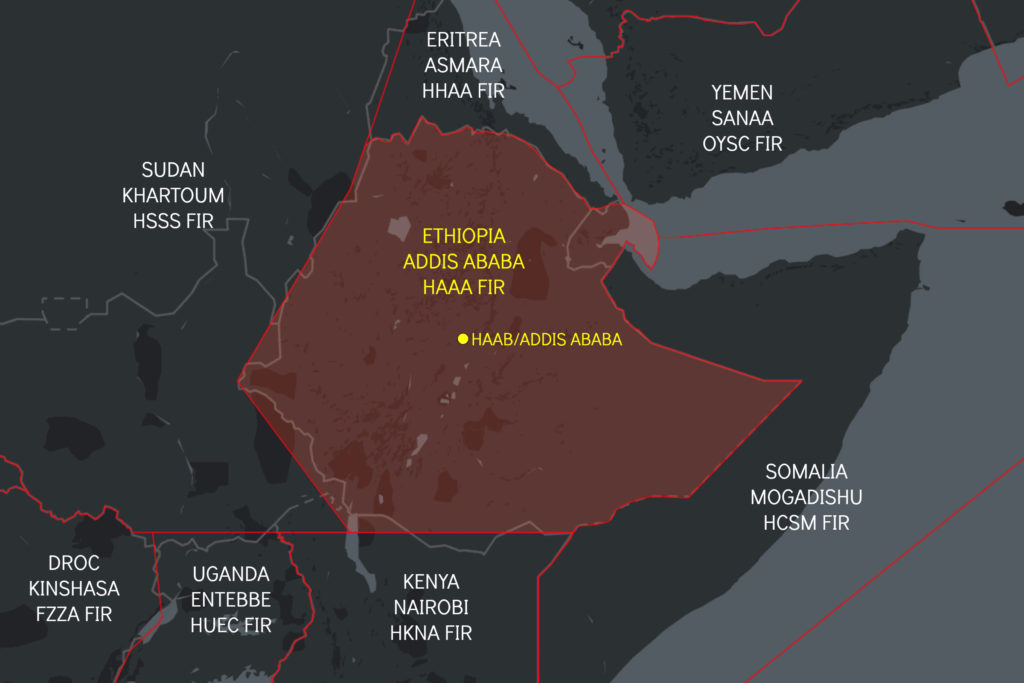
- OPSGROUP alert for the Addis Ababa FIR
- Airspace risk – unrated controllers, some foreign and unfamiliar
Air Traffic Controllers are on strike in Ethiopia, and Ethiopia would prefer that you don’t know this. We, as OpsGroup, would prefer that you do.
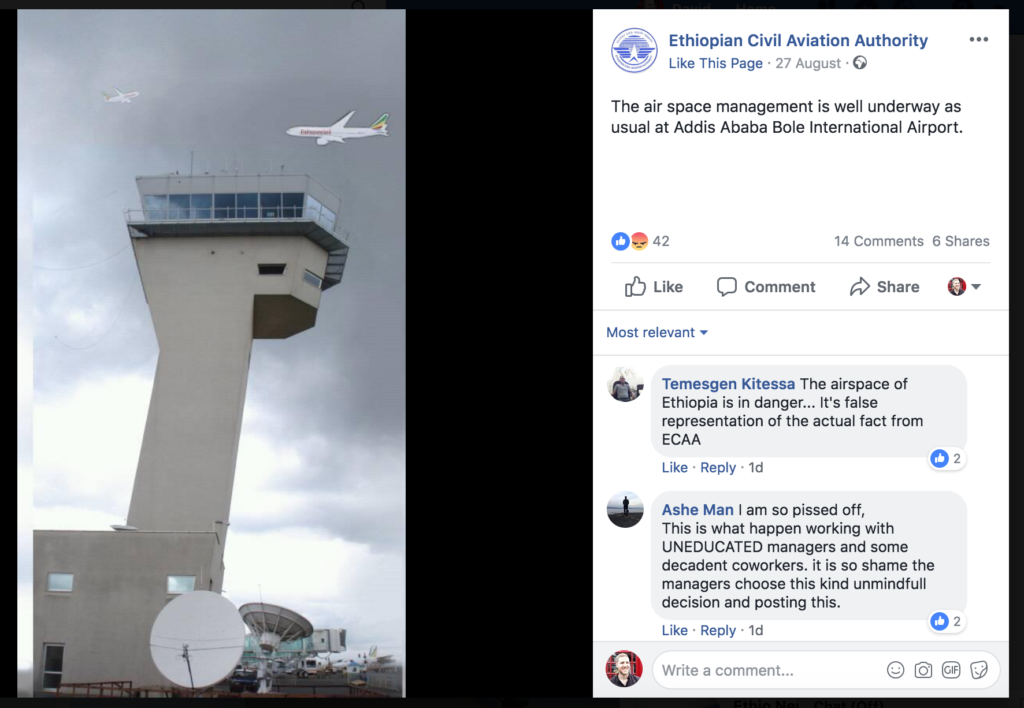
Ethiopia would also prefer that it has no impact on the flight operations of its national carrier, Ethiopian Airlines. Therefore, they have drafted in foreign controllers to replace the strikers, issued no Notams, hushed any publicity, and proactively declared ‘operations normal’ (complete with bizarre, hand drawn airplanes).
European airlines – and frustrated passengers – will watch with great interest, thanks to their own ATC strike woes: regular stoppages by French, Italian, and Greek controllers have this summer, once again, been the source of massive cancellations, reroutes, and delays. Has Ethiopia found the golden elixir, the magic solution to a long-running problem? Is this how to handle a strike by your nations’ Air Traffic Controllers?
It absolutely is not. It is a catastrophic misjudgement, creating a safety risk in the Addis FIR and at Ethiopian Airports for pilots and passengers alike. Ethiopian airspace, this week, is most definitely not ‘operations normal’ – it is unpredictable and unsafe, staffed by unrated, inexperienced controllers, many from abroad – evidenced already by alarming reports of close calls from adjacent Area Control Centers – read on.
The facts are this: faced with an upcoming strike by ATC, Ethiopian Airlines – now Africa’s largest airline – formed what in the boardroom might have seemed a workable plan: Recruit a bunch of controllers from other countries, fly them in to Addis, and have them do the work of the striking staff.
The first batch of foreign controllers came from the Democratic Republic of the Congo, a small group described by the local controllers, unsurprisingly, as mercenaries. When the strike started at 7am this past Monday morning, they were ready to go. Not content with stopping there, the requests from ECAA – the Ethiopian Civil Aviation Authority – for more external controllers went out thick and fast, like an Ambien fuelled shopping spree on Amazon. 30 requested from Sudan, 24 from Kenya. More from Zimbabwe, Malawi. Finding those requests rejected, and resistance from other ATC agencies, the biggest request yet: 120 controllers from ASECNA.
The plan, commercially, is understandable. The wish to keep their airplanes flying is not endemic to Ethiopian Airlines. British Airways, Ryanair and Easyjet, have all made very public their frustrations with ATC strikes. An association, A4E, was formed to fight the problem at European level.
But here’s why the Ethiopian solution doesn’t work.
And as a former Air Traffic Controller, and Airline Pilot, I can tell you why.
Air Traffic Control is complex. That’s not a secret. On average, it takes a controller three months to gain a ‘rating’, or qualification, for a specific piece of airspace; that’s how long it takes to become comfortable with the 4D picture in front of you to provide a flawless ATC service. More complex airspace could take six months.
You have to learn each corner of your bit of sky. Learn the rules of the sector, learn the agreements you have with other centres about how you will receive and present traffic at the boundary. But the most important thing you learn is how the traffic flows.
ATC is not an aerial traffic battle whose landscape changes each day. It is not a web of complex contrails that, seen from the ground, appear to merge and diverge at random. The traffic flow is a largely predictable set of events, where the same airlines are operating on the same routes – providing a basis for us, as controllers, to learn the patterns of the flow, and to learn a trick for every trajectory.
This is key. It’s been 15 years since I worked the North Atlantic flow in Shannon, but I remember the callsigns, the flows, and how to handle them, like an indelible challenge and response game in my mind.
“Shamrock 37J, airborne Shannon” : “direct to Strumble, climb him to 270”.
“Belfast departure for Tenerife” : “stop him low, get him under the NAT traffic”.
“Two converging at LIFFY” : “Drop the Speedbird, he’s for Manchester”.
Humans learn patterns. This is how ATC works. We fill a bucket full of “stuff we’ve seen before”, leaving us free to concentrate on the few things we haven’t. This is the flow. If you watch 737’s fly up the Hudson on a hot summer morning, this is the La Guardia flow. Not an inch left or right. Heading into Amsterdam? “Direct to Pampus, down to FL70”. One after another.
This is why we need three months to learn the airspace. For the flow. And this is why, when I found myself in New Zealand, learning to operate as an Air Traffic Controller far away from Shannon, I was floundering, like one of those dreams where you running but standing still. I am a controller, but I can’t control. I don’t know the airspace, and I don’t know the flow. Slowly, over the months, geography takes shape, traffic patterns show themselves, situations become seen. I start to get a sense of distance and time on my scope – or scopes, because New Zealand is long and thin I have to reorientate my thinking north-south, rather than east-west, as in Shannon. Out of the mist of training, I am a controller again, but it takes time. A lot of time.
Ultimately, I can reach the point where I can do my job – the real job of an Air Traffic Controller – to be familiar enough with the airspace and traffic that I have “the picture”. The full situational awareness, with most climbs, descents, speeds, and vectors being routine and familiar, means I can spot the something that’s off, wrong, going to develop into a conflict, and do so intuitively, like a sixth sense. Air Traffic Control is an art, it’s a dance. You don’t do it by complex calculations in your head, you don’t need a computer. It’s the visual in front of you – radar or tower – coming to life in your brain, you feel it, and the solution becomes instinctive.
And this is why you can’t bus in a set of replacement controllers, shuffle them down the corridor into the radar room, and up the stairs to the tower, and expect a safe, efficient, and orderly flow of traffic.
Controllers know the power of the strike. In most countries, it is used rarely, and fairly. They understand the impact on airlines and passengers. There are many other forms of industrial action a controller can take – like a training ban, an overtime ban – before reaching the point of actually stopping work.
Commerce will always find a way to continue. Safety is different, and delicate. It must be nurtured and protected. When the two collide head on – the commerce of keeping an airline flying, vs. the safety of an established, effective Air Traffic Control system – safety must take precedence. Here, safety means accepting the strike, as is – and working with the controllers, quickly, to find a solution. Let them be heard.
We’ll keep this page updated with the latest situation on the Ethiopian ATC strike. Reports that we have received so far are as follows:
- Controllers in adjacent ACC’s are reporting lack of adherence to Letters of Agreement – seeing aircraft with 4 minutes instead of 10 minutes separation.
- RA reported by Kenya ATC between two airlines on Wednesday.
- Kenya and Sudan reported loss of separation and poor coordination and transfer of traffic at their FIR boundaries with Ethiopia.
- Retired and Management controllers, who appear to have never rated or validated in position, are also being used, though unqualified for Addis.
We were first alerted to this issue by a Fox. Many of you know that we are Fixing Notams. The lack of Notams in this situation, is an exceptionally clear example of point 1 in the “Why” of the Notam Problem. Sometimes, we can’t trust the state to tell the truth. And this is a clear example.
Thankfully, our network of Foxes – undercover ATCO’s, pilots, and dispatchers – is growing, and reporting on things just like this, so that we can tell you what’s really going on. Keep reporting.
Further reading
- Tell us anything additional we should know – news@ops.group
- Monitor #ops-alerts in your member Dashboard, and Slack.
- Contact the author: Mark Zee.
More on the topic:
- More: How to survive a French ATC strike
- More: The Curious Case of the Bonus French ATC Strike
- More: Africa ATC Strike
- More: Morocco ATC Strike Cancelled!
- More: Ethiopia Airspace Update
More reading:
- Latest: OPSGROUP is hiring! Wanted: Junior International Ops Specialist
- Latest: LOA Guide for US Operators
- Latest: NAT Ops: Flying the Blue Spruce Routes
- Safe Airspace: Risk Database
- Weekly Ops Bulletin: Subscribe
- Membership plans: Why join OPSGROUP?












 Get the famous weekly
Get the famous weekly 





