Update Nov 2025: Somalia-Somaliland Airspace and Permit Dispute
Be aware of an ongoing authority dispute in the north of the HCSM/Mogadishu FIR. Both Somalia and the self-declared state of Somaliland have issued conflicting instructions for overflights. From Nov 10, Somaliland says all flights require PPR from its own CAA, while Somalia has reaffirmed through an AIC that it controls the entire FIR and operators should follow its AIP.
Expect mixed messages on permit requirements near northern Somalia and the Hargeisa region. The Somali CAA remains the only internationally recognised authority for all Class A airspace above FL245 – be cautious of conflicting or unauthorised clearances.
For background on this long-running dispute and its impact on ATC safety, see safeairspace.net.

Ongoing since Feb 2024: ATC Conflict in Somalia
Key information for Flight Crew
Over the weekend, OPSGROUP has received at least 10 reports of aircraft within the Mogadishu FIR being contacted by a ‘fake controller’ on the same frequency, issuing conflicting instructions.
Crews have been issued climb and descent clearances that are not from the sector controller. Incidents have been reported mostly in the northern part of Mogadishu airspace.
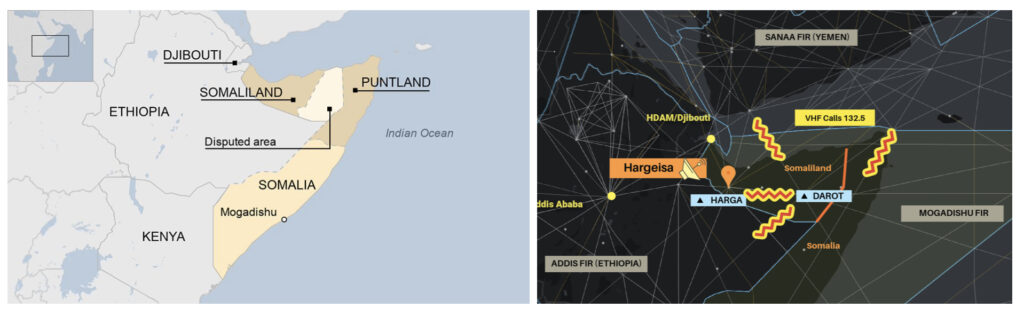
The situation emanates from a political dispute between Somaliland and Somalia, two different countries, though the former does not have international recognition. Both countries now claim authority over the Mogadishu FIR.
Quick Summary – ATC Conflict in Somalia
- This affects aircraft transiting the Mogadishu FIR
- Enroute aircraft are being addressed by competing ATC units on the same frequency.
- Numerous aircraft have received climb/descent instructions from unauthorized ATC units.
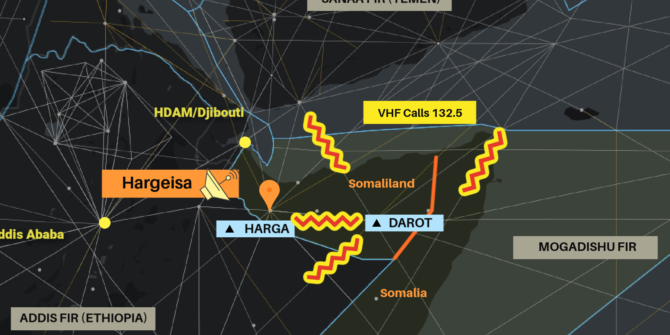
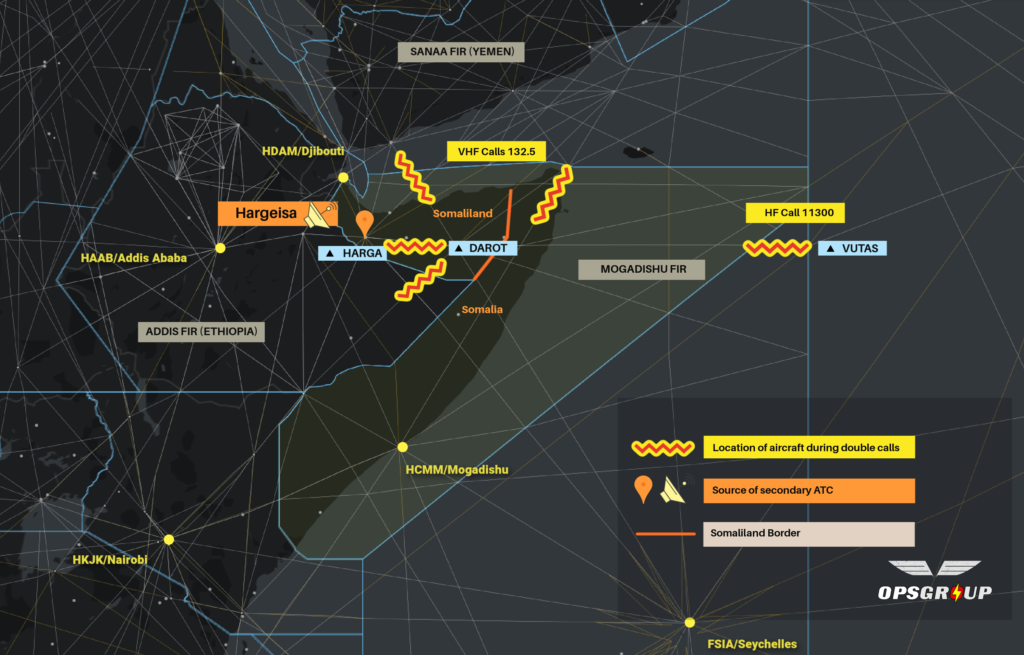
- Location: Primarily within radio range of Hargeisa (VHF 132.5), also via HF (11300)
OPSGROUP Members
In your Dashboard you’ll find the full Risk Warning, including Crew Reports, Maps, Analysis, and Guidance. If you can’t access, just email the team and we’ll send you a copy.
Download the Risk Warning (PDF, 9 pages, 2Mb)
Analysis
(Excerpt from the Risk Warning in your dashboard)
The background to the situation is an escalating political dispute between Somaliland and Somalia. Somaliland has been an independent country since 1991, but without international recognition. Somaliland has to date maintained control over its airports, but Somalia controls the upper airspace from Mogadishu.
In January 2024, Ethiopia signed an agreement with Somaliland, essentially exchanging port rights on the Red Sea for recognition of their country. This was met with condemnation by Somalia. Somalia, in response, began restricting movements into Somaliland by way of denying airspace entry to the Mogadishu FIR in some instances. This has led to Somaliland declaring its right to exercise control over their airspace.
The net result is an airspace dispute between the two territories. Both Somalia and Somaliland now claim the right to control traffic. This is why crews have been contacted by other “controllers” on 132.5 (VHF) and 11300 (HF). Although it is likely that these other “controllers” are genuine Air Traffic Controllers, they are operating outside their area of jurisdiction as things stand.
Currently, the authority over the entire Mogadishu FIR is Mogadishu Control. They remain the sole authority to control, coordinate, and provide ATS services in the Upper FIR. The secondary transmissions are coming from Hargeisa in Somaliland. Although the motive for these transmissions can be understood, they present clear danger to enroute traffic. The transmissions appear to attempt to mimic Mogadishu rather than present as “Hargeisa Control”, “Somaliland Control”, or any clear differentiator from Mogadishu.
It would also appear from the reports that we have received, that the control instructions are not being issued to de-conflict traffic, but rather to create confusion. This may be an effort to draw attention to the airspace issue, but could have tragic consequences. For flight crews, we follow with some guidance to mitigate the situation.
The situation is volatile and may escalate. On Sunday, February 18, an AIS Officer from Somaliland, working in Mogadishu, was found dead at his home. His death appears related to this situation.
Avoidance of Mogadishu airspace would provide ultimate safety, and if the situation continues, would be wise.
[Excerpt, see full Risk Warning for crew reports received, maps, guidance]



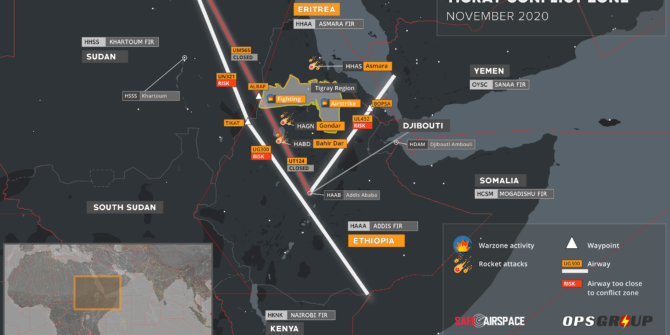
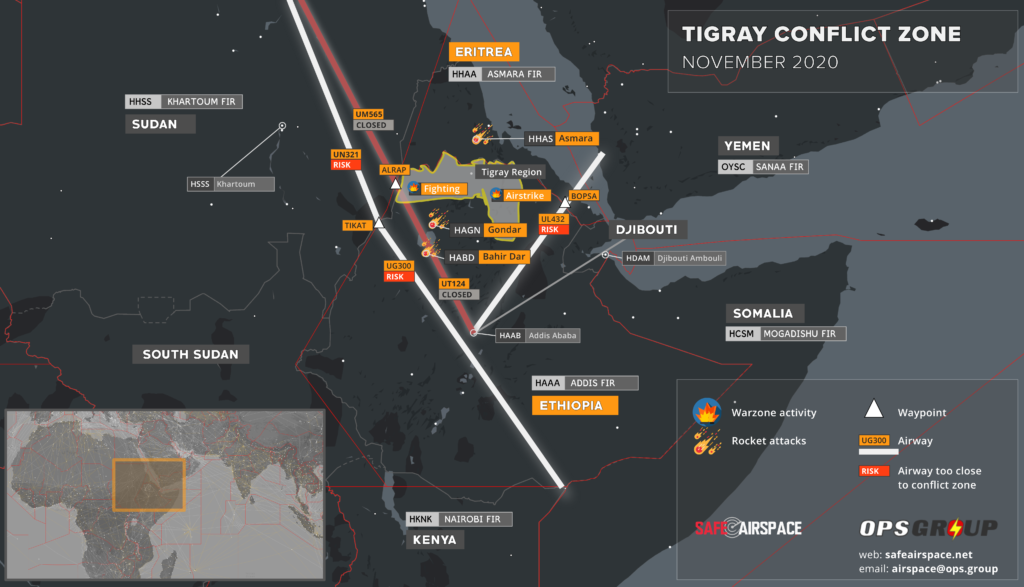







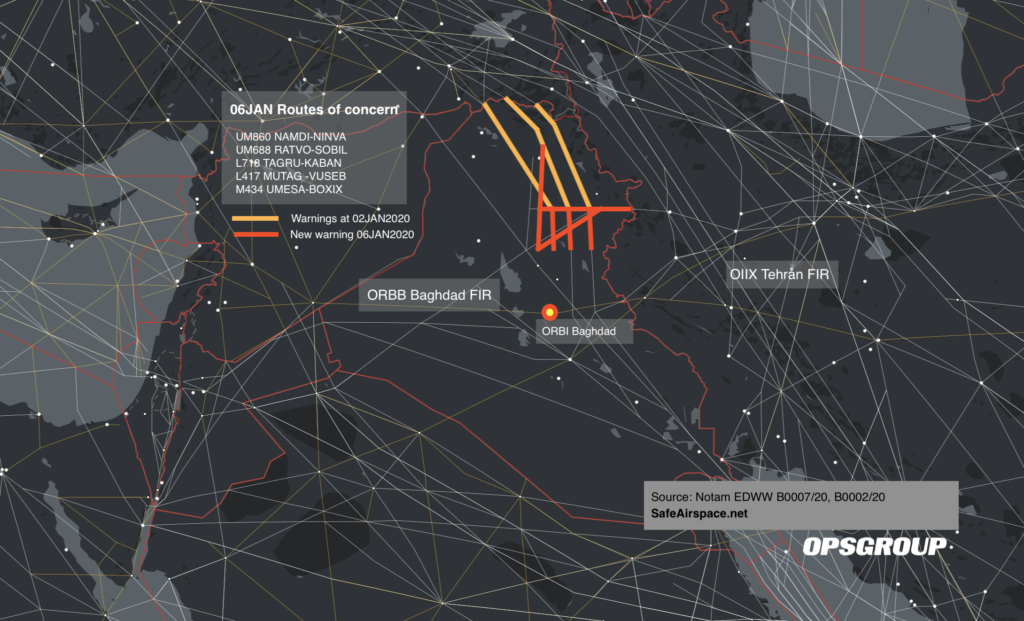
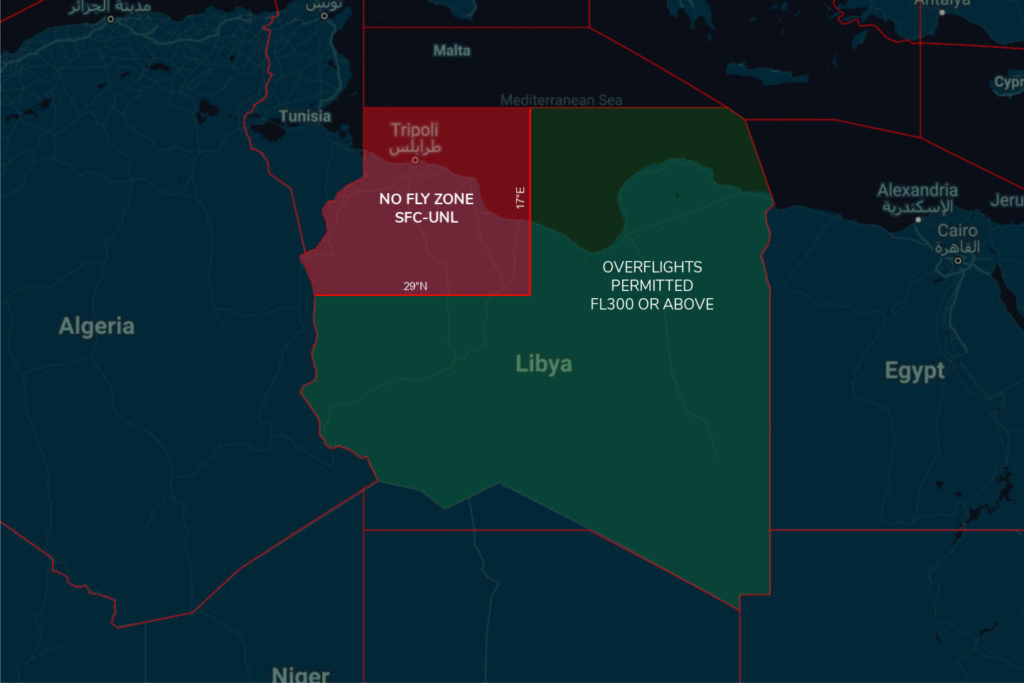

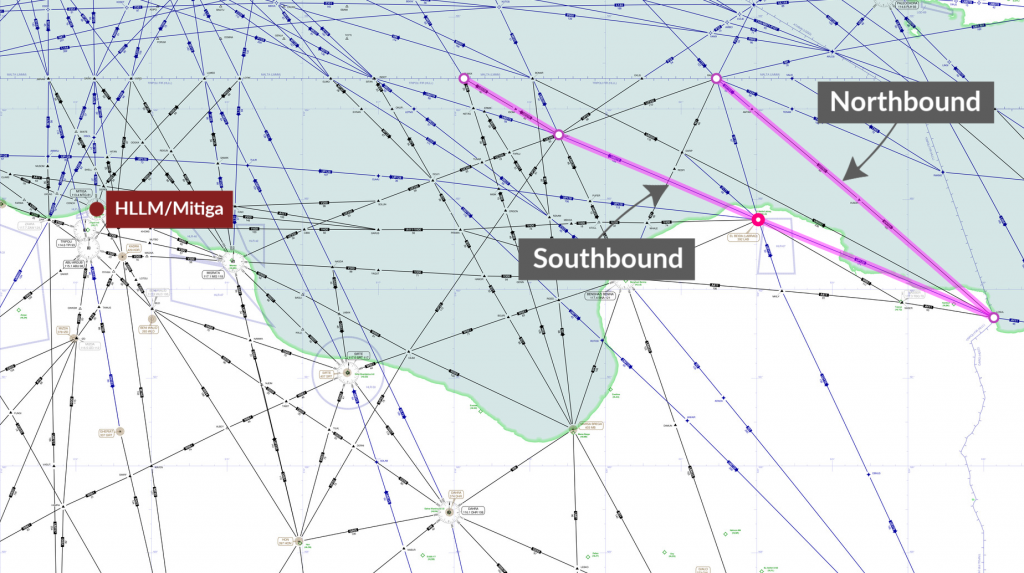 Northbound: LOSUL UP128 LAB UM979 RAMLI UZ270 OLMAX (even levels)
Northbound: LOSUL UP128 LAB UM979 RAMLI UZ270 OLMAX (even levels)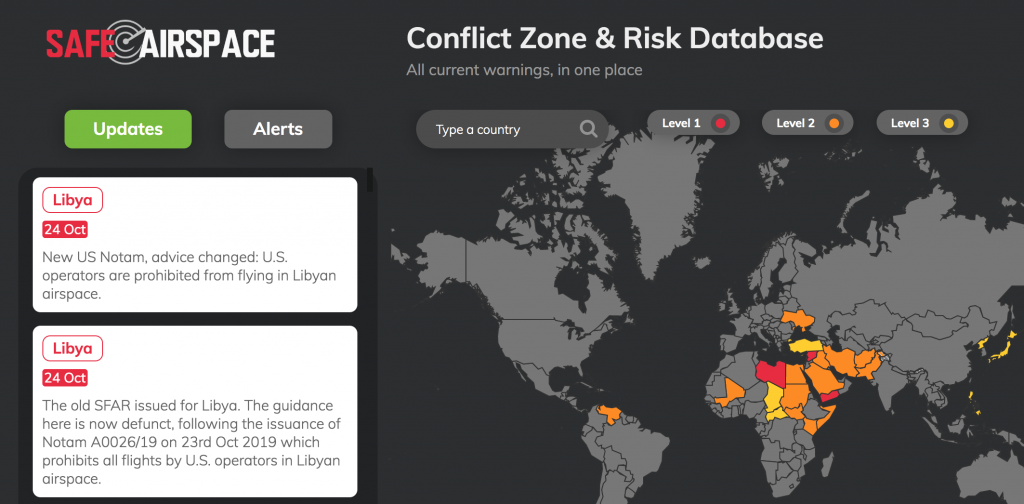
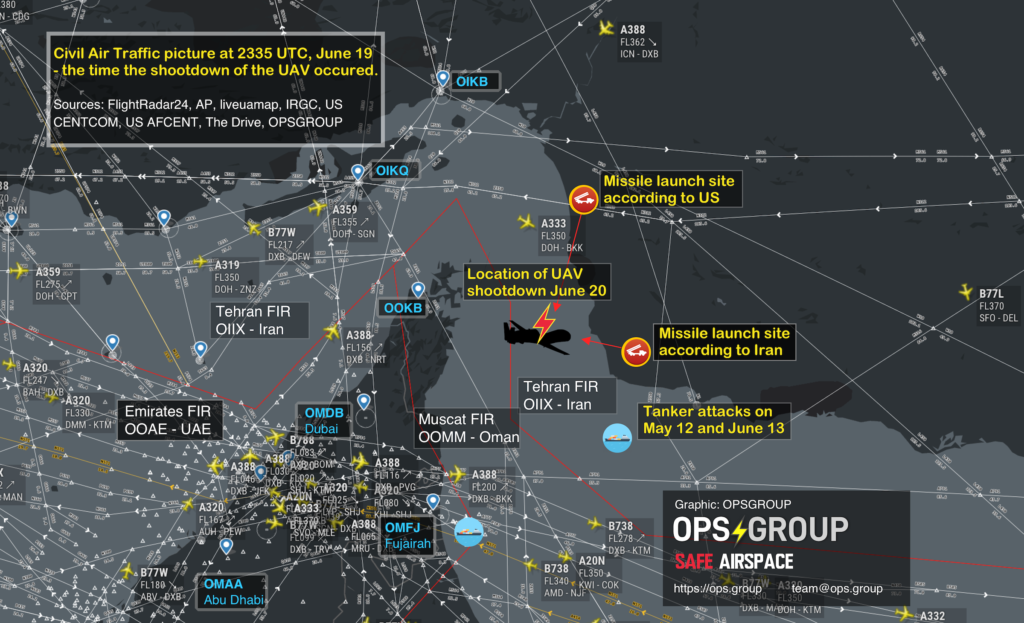
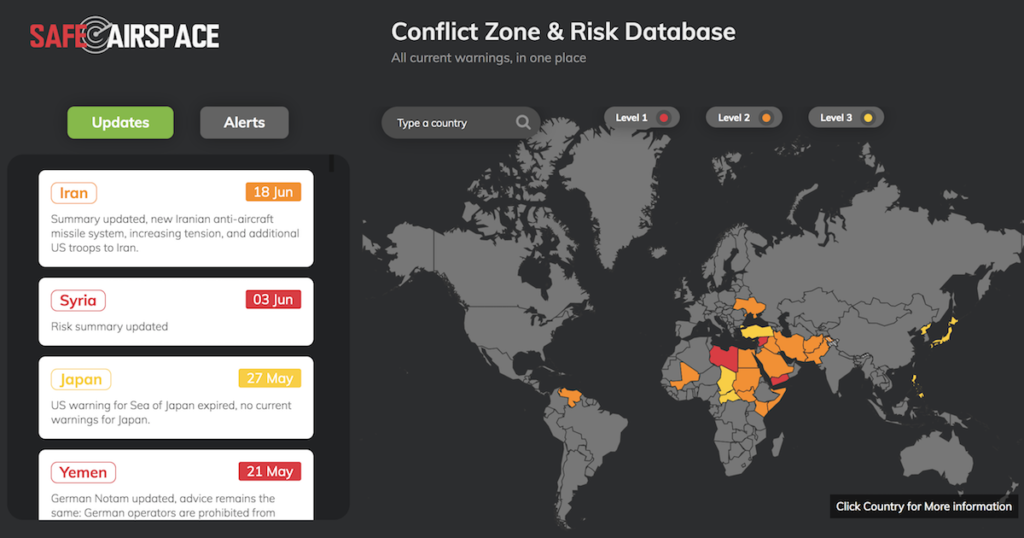
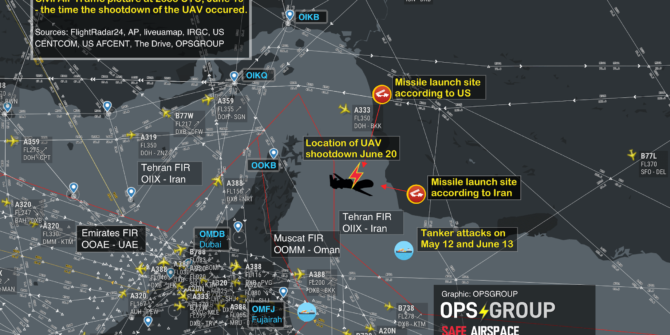
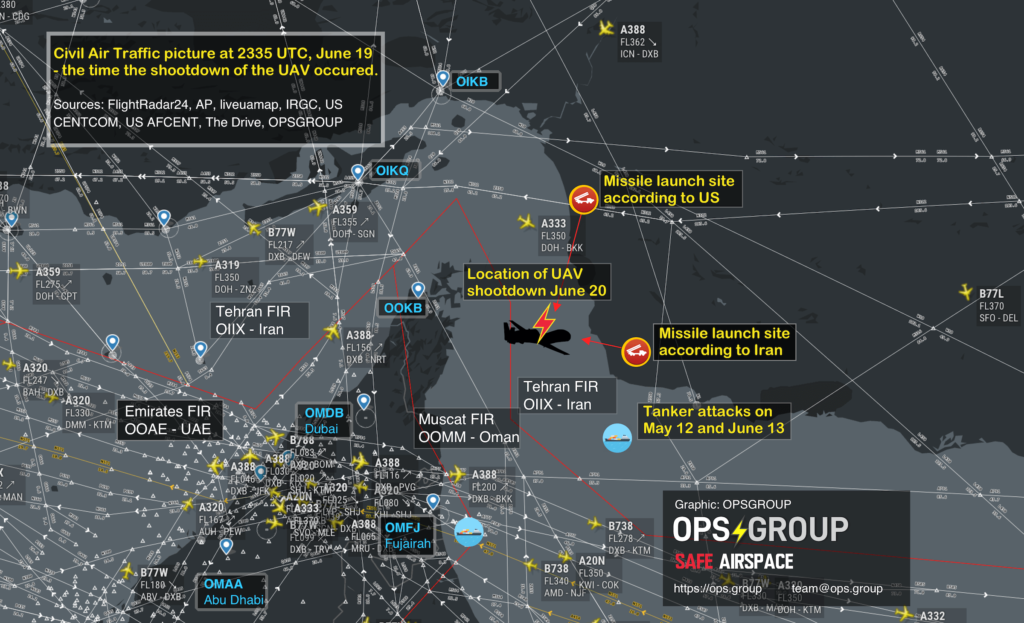
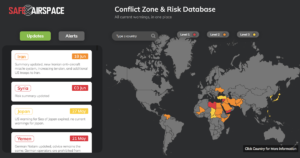







 5th September, update:
5th September, update: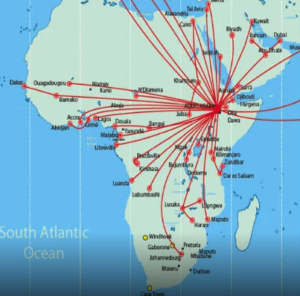 Here are some more updates since our last article:
Here are some more updates since our last article: The ECAA also outlined that the national carrier, Ethiopian Airlines, has “
The ECAA also outlined that the national carrier, Ethiopian Airlines, has “
 What are surface-to-air missiles, and who has them?
What are surface-to-air missiles, and who has them?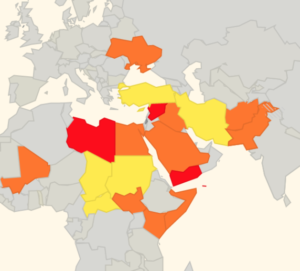 There is some evidence to suggest that more States are starting to provide better guidance and information to assist operators in making appropriate routing decisions, but we think this still has some way to go.
There is some evidence to suggest that more States are starting to provide better guidance and information to assist operators in making appropriate routing decisions, but we think this still has some way to go.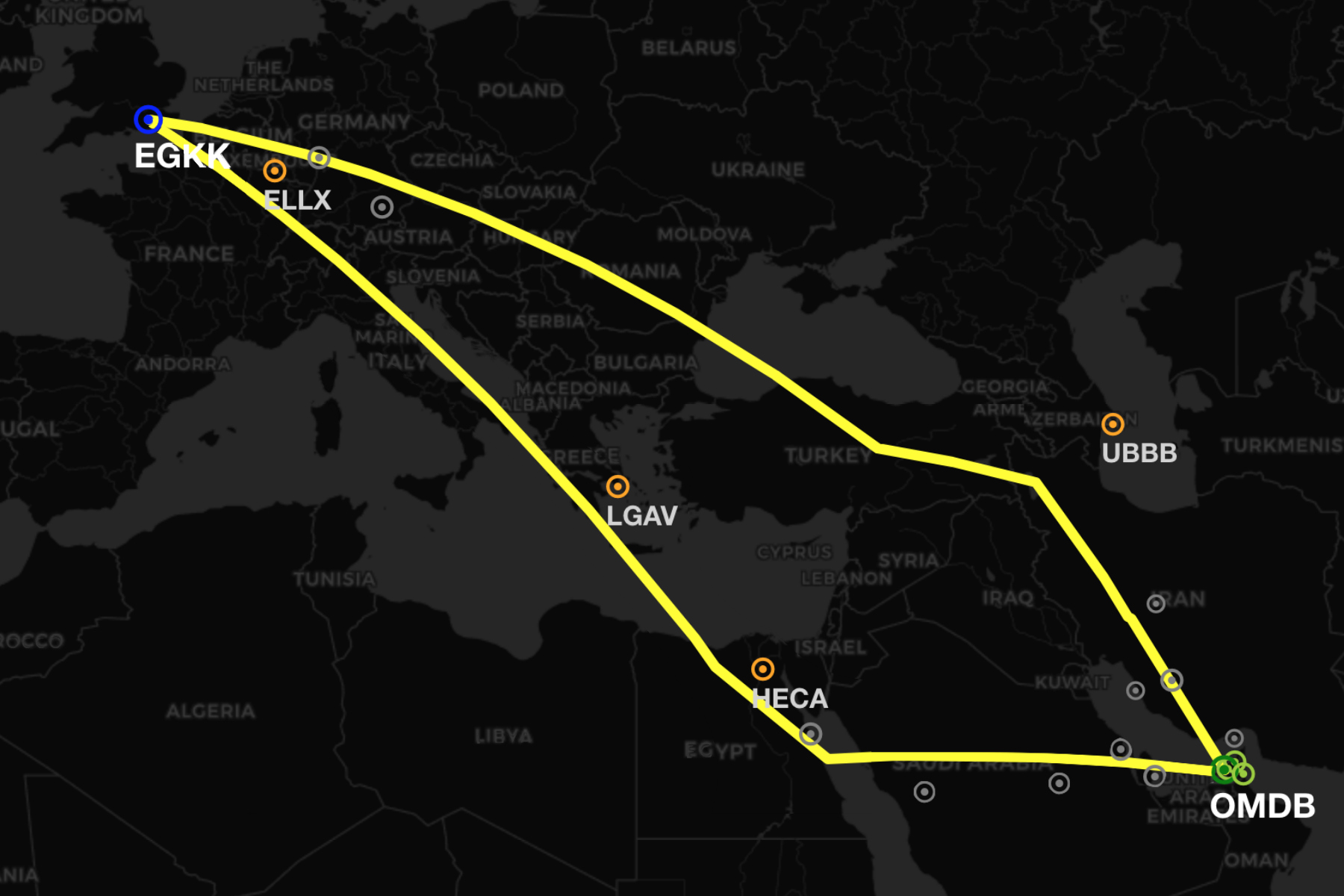
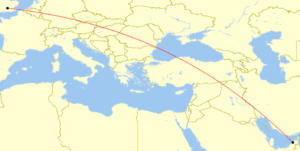 There are more business aviation operators flying between the Middle East and Europe than ever before. So we took the time to look over the route options between the two regions. For our example we will be using a flight from Dubai to London, but similar operational considerations are valid for the plethora of route combinations through this whole region.
There are more business aviation operators flying between the Middle East and Europe than ever before. So we took the time to look over the route options between the two regions. For our example we will be using a flight from Dubai to London, but similar operational considerations are valid for the plethora of route combinations through this whole region.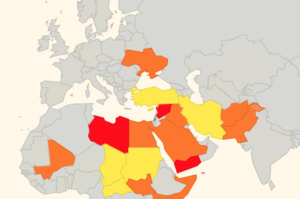
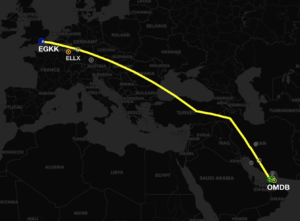 Safety: Both
Safety: Both 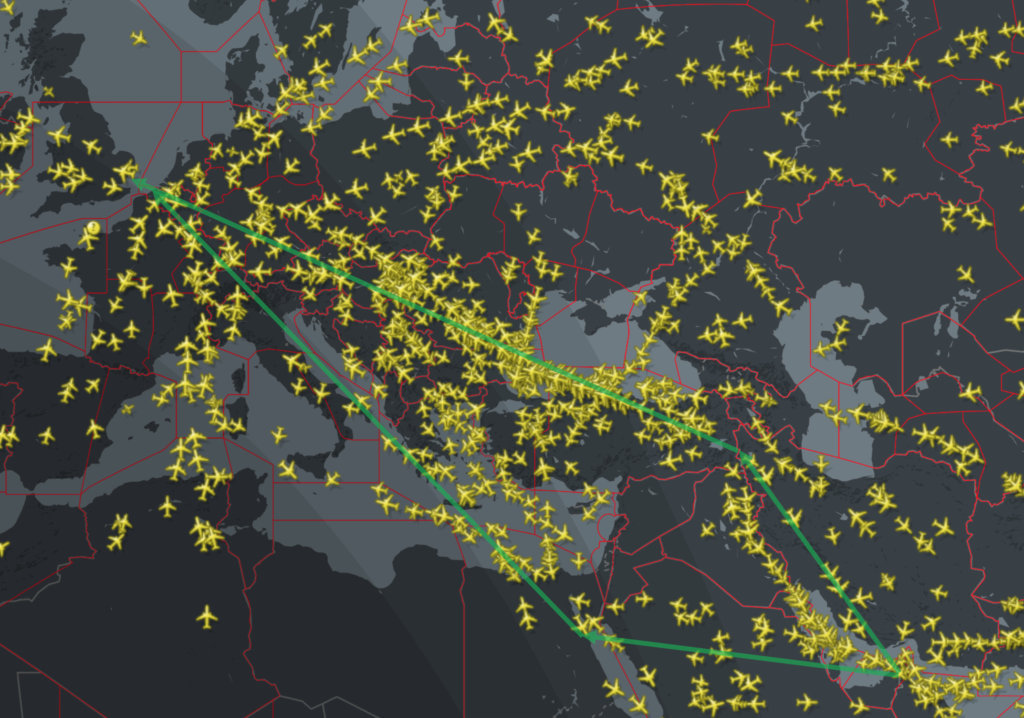
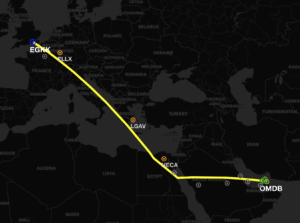 Safety: In terms of airspace warnings and risk, this route is slightly better. We have rated
Safety: In terms of airspace warnings and risk, this route is slightly better. We have rated 
 opean Aviation Safety Agency (
opean Aviation Safety Agency ( The regulation that a plane coming from a non EU country must have a
The regulation that a plane coming from a non EU country must have a 


 Beyond this alert and NOTAM though; nothing else happened. A few days later, the
Beyond this alert and NOTAM though; nothing else happened. A few days later, the  What has happened in the few weeks since then?
What has happened in the few weeks since then?
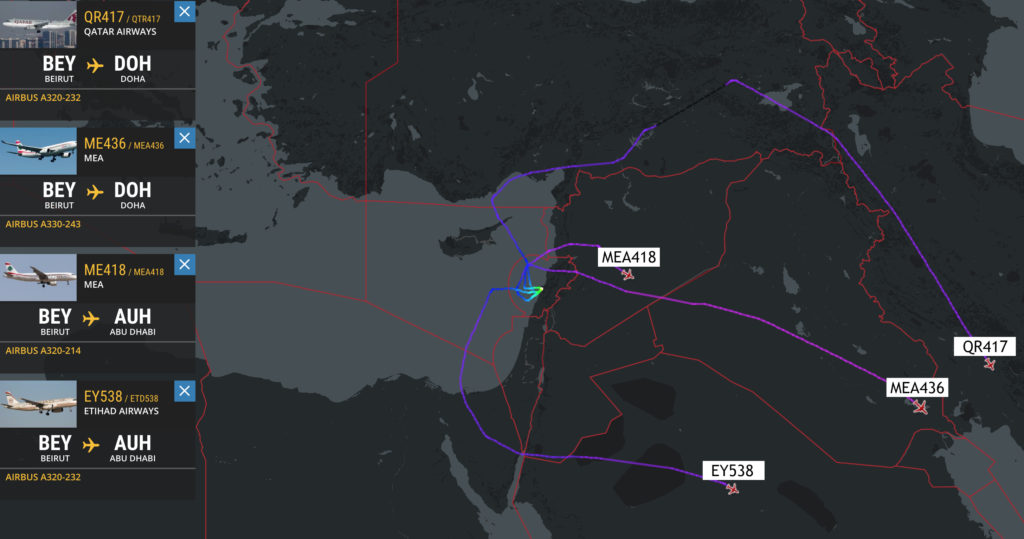
 These MEA overflights are of interest. The airline is a member of the
These MEA overflights are of interest. The airline is a member of the