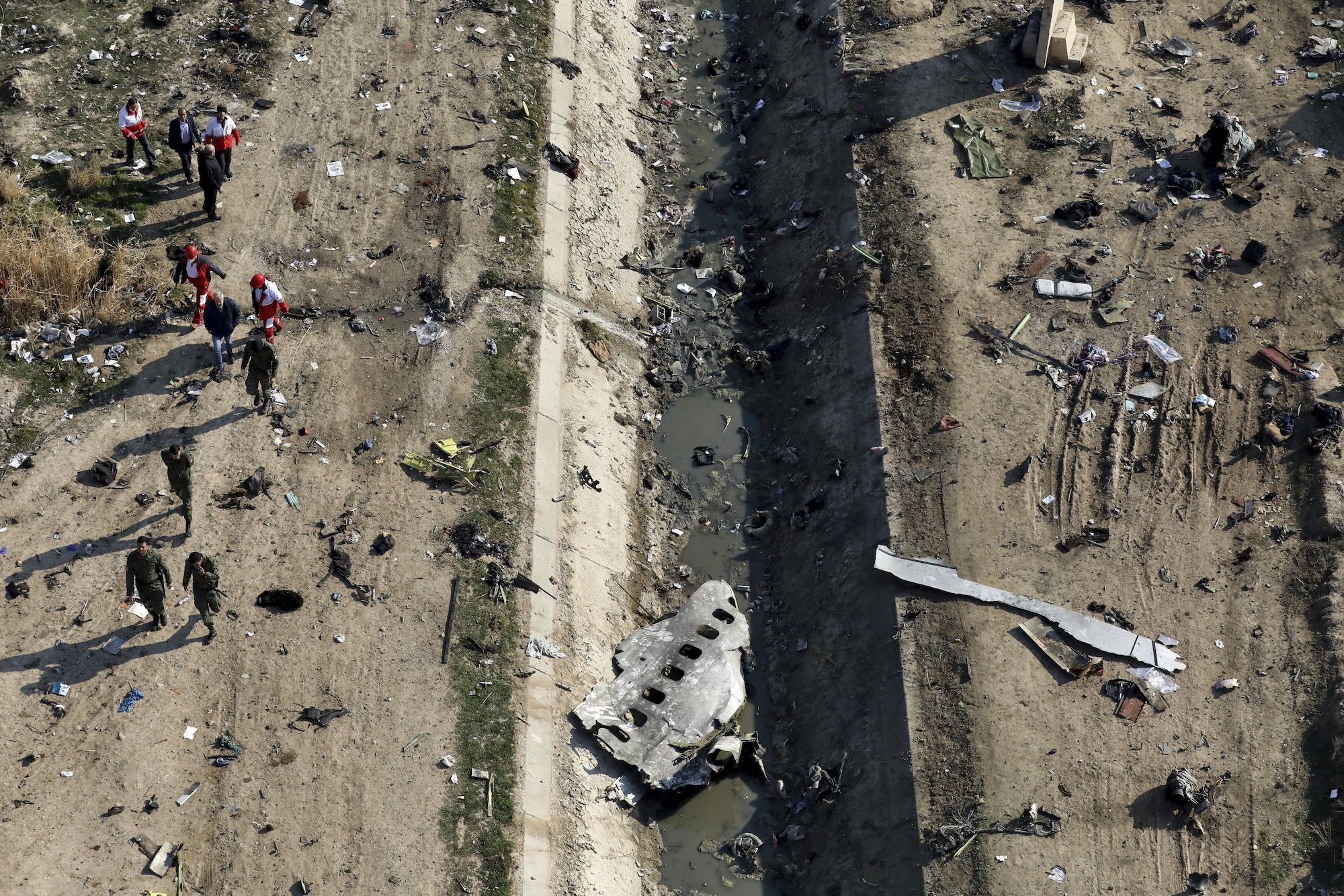
Iran has released its first official report into the shoot-down of UIA flight 752 in Tehran on Jan 9. They blame a misaligned missile battery, miscommunication between troops and their commanders, and a decision to fire without authorization as the major factors which led to the shoot-down of the plane by Iran’s Revolutionary Guard.
All 176 people on board were killed when the plane was hit by two missiles shortly after take-off in Tehran.
Iran initially denied responsibility for the incident, only admitting fault days later after Western nations presented extensive evidence that Iran had shot down the plane.
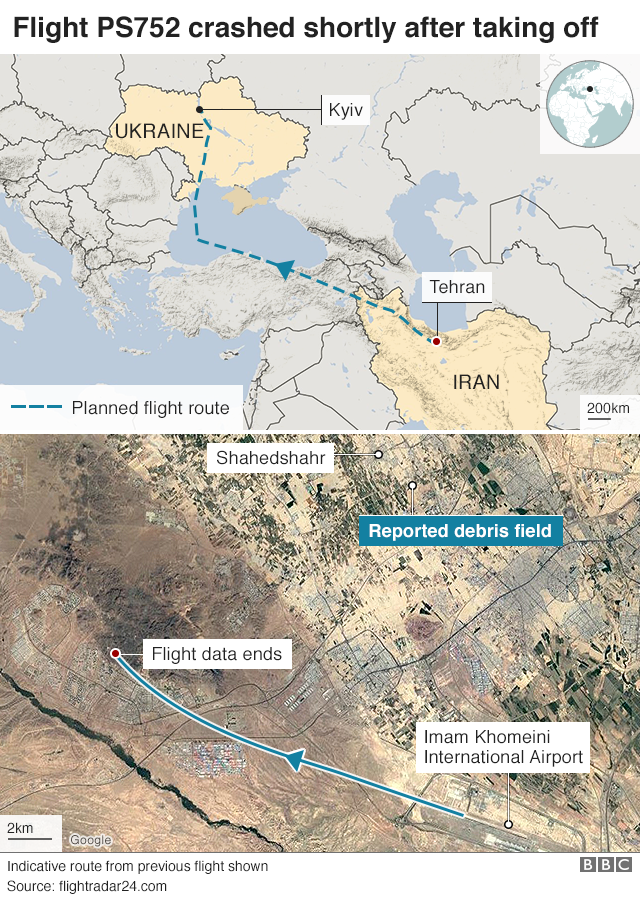
Iran’s air defences had been on high alert at the time. Just hours prior to the shoot-down, the US FAA issued “Emergency Order” Notams banning all US operators from overflying the airspace of Iraq and Iran. This was in response to an Iranian missile strike on US military bases in Iraq, which had just occurred the same night.
A full version of the report has not been made publicly available, but excerpts have been published by state news agency Fars. It places the blame entirely on those manning the missile system, and details a series of key moments where the shoot-down could have been avoided, the main two being:
- The surface-to-air missile system had recently been relocated and was not properly calibrated. As a result, it misidentified the civilian plane as a hostile object.
- Those manning the system could not communicate with their command centre, and fired on the plane without receiving official approval.
“If each had not arisen, the aircraft would not have been targeted,” the report said.
It also notes that the flight had done nothing unusual prior to the missile launch, with its transponder and other data being broadcast. It claims that the troops manning the missile system tried to contact the Coordination Centre with details of a potential target but they did not manage to get through, and that firing on the aircraft under these circumstances was against approved protocol:
“The system operator began analysing the observable information and categorised the detected target as a threat… At 02:44:41, without receiving any response from the Coordination Centre, the air defence unit operator fired a missile at the threatening target he had detected… Under the applicable procedures, if the defence system operator cannot establish communication with the Coordination Centre and does not receive the fire command, they are not authorised to fire.”
After repeated delays, Iran has said it will release the aircraft’s black box to officials in France on July 20, where Ukrainian and French experts are expected to examine it.
Airspace warnings
In the days and weeks following the shoot-down, several other countries followed the US in issuing airspace warnings of their own for Iran, including: the UK, Ukraine, Canada, Germany, and France. The US and Ukraine are the only countries to have issued outright flight bans on Iranian airspace, but all the others advise against landing or overflying the country at the lower flight levels. Check SafeAirspace.net for a full summary.
Traffic flows
It’s worth considering that most airlines other than Middle Eastern carriers are still avoiding Iran. For traffic that normally operates through the Tehran FIR, a predominant alternative for east-west flights into the Dubai area is a southerly routing via Saudi Arabia and Egypt. There are warnings for both of these airspaces as well. Northerly reroutes for Europe-Asia flights are predominantly using a Turkey-Armenia-Azerbaijan-Turkmenistan routing. If entering Afghanistan airspace, note the current warnings there too.
Unfamiliar routes
For many operators wanting to avoid Iran, you may be using routes that are unfamiliar. Take the time to ensure you have the full package of charts, are aware of the risks in each FIR, are aware of the potential for GPS outages en-route (especially in the Turkish, Tel Aviv, Amman, and Jeddah FIRs), and have considered drift down over mountainous areas on the northerly routes.
Advice
Every air operation different. We know OPSGROUP has a huge variety of members – some conducting routine airline flights, some business aviation, charter flights, private ops, military, government flights. Therefore, offering blanket advice is difficult. You must undertake you own risk assessment, but paying close attention to the international warnings as well as what other carriers are doing is a good place to start.
On SafeAirspace.net, we continue to list Iran as Level One: Do Not Fly. The same goes for Iraq. Outside those two countries, just consider carefully what connections to the current situation there may be. Nowhere in the Middle East is without some level of risk.
More on the topic:
- More: April 2024: Israel/Iran Situation, All Call active
- More: Airspace Risk Update – Important Changes You May Have Missed
- More: Get ready for more North Korean missiles
- More: Airspace Risk: Conflict Zones and Security in 2023
- More: Ukraine-Russia Spillover Risks: Nov 2022
More reading:
- Latest: OPSGROUP is hiring! Wanted: Junior International Ops Specialist
- Latest: LOA Guide for US Operators
- Latest: NAT Ops: Flying the Blue Spruce Routes
- Safe Airspace: Risk Database
- Weekly Ops Bulletin: Subscribe
- Membership plans: Why join OPSGROUP?











 Get the famous weekly
Get the famous weekly