Key Points
- One of Iceland’s volcanoes (10nm southwest of BIKF/Keflavik) is showing signs it’s about to erupt.
- If it does, NAT crossing traffic is likely to be affected at short notice.
- ICAO have a Contingency Plan ready to go if it does erupt (PDF below).
- Pilots and Operators: There is a list of things to watch out for if you do fly through volcanic ash, and a recommended procedure to follow.
Iceland is on high alert for an imminent eruption at one of the volcanoes on the Reykjanes Peninsula – a stone’s throw southwest of Keflavik. If it does erupt, it has potential to seriously impact North Atlantic traffic.
The last time this happened in 2010, the (try pronouncing this one) Eyjafjallajökull volcano closed almost every country’s airspace in Western Europe in the weeks that followed. Nearly 100,000 commercial flights were grounded.

One of the few flights not to be impacted by the volcanic ash in 2010.
Where are we talking about?
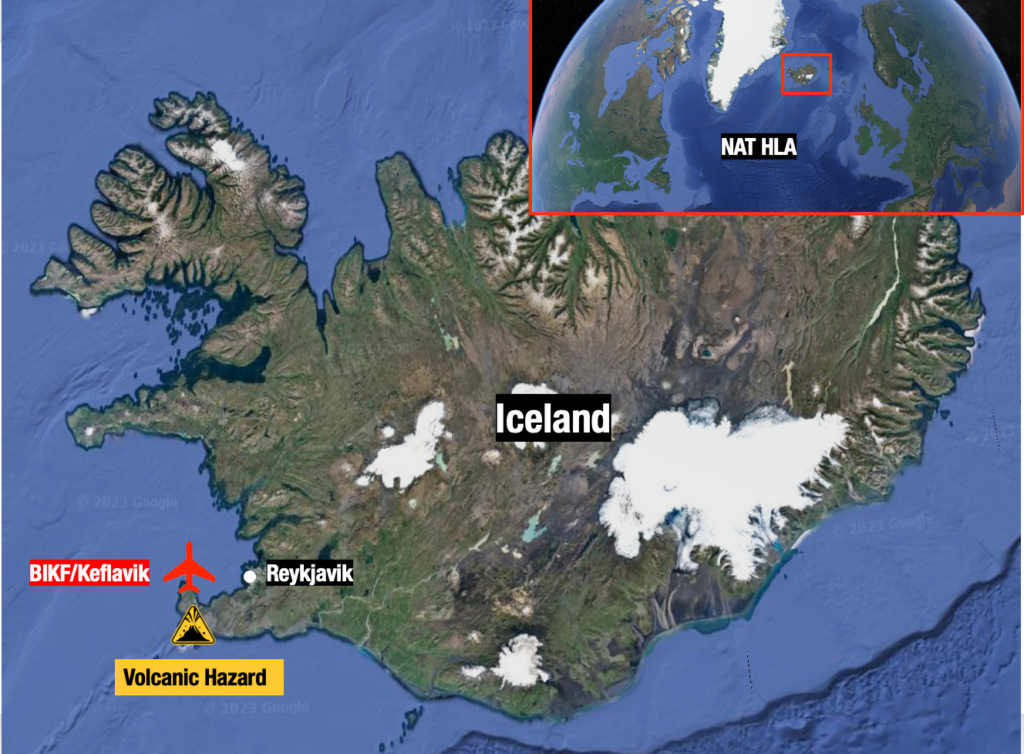
What happens if it erupts?
So far, it’s just a warning. But it’s credible enough for Iceland to declare a state of emergency. Recent earthquakes in the area are an ominous sign. If it does erupt, there are several possible scenarios that could affect air traffic.
- BIKF/Keflavik may close. Unlike previous eruptions, this one is just 10nm away from the airport and a little further from the Icelandic capital, Reykjavik. Aside from being a major airport in its own right, BIKF is a commonly used ETOPS/EDTO alternate for traffic crossing the NAT.
- Part of the NAT HLA may become unusable depending on the spread of ash. More southerly routes than usual may become a requirement which means extended flight times and more fuel.
- Major airspace closures could occur for an extended period of time. The European mainland may once again be in the firing line, thanks to the mid-latitude westerlies.
Yeah but what ACTUALLY happens?
If the volcano warning goes to code RED (it’s currently code ORANGE), that basically means an eruption has started. In this case, the airspace within a 120nm radius will close, until they confirm there’s no ash cloud. They currently think there is a 15km long line where magma is flowing and moving towards the surface – an eruption could happen anywhere close to that line.
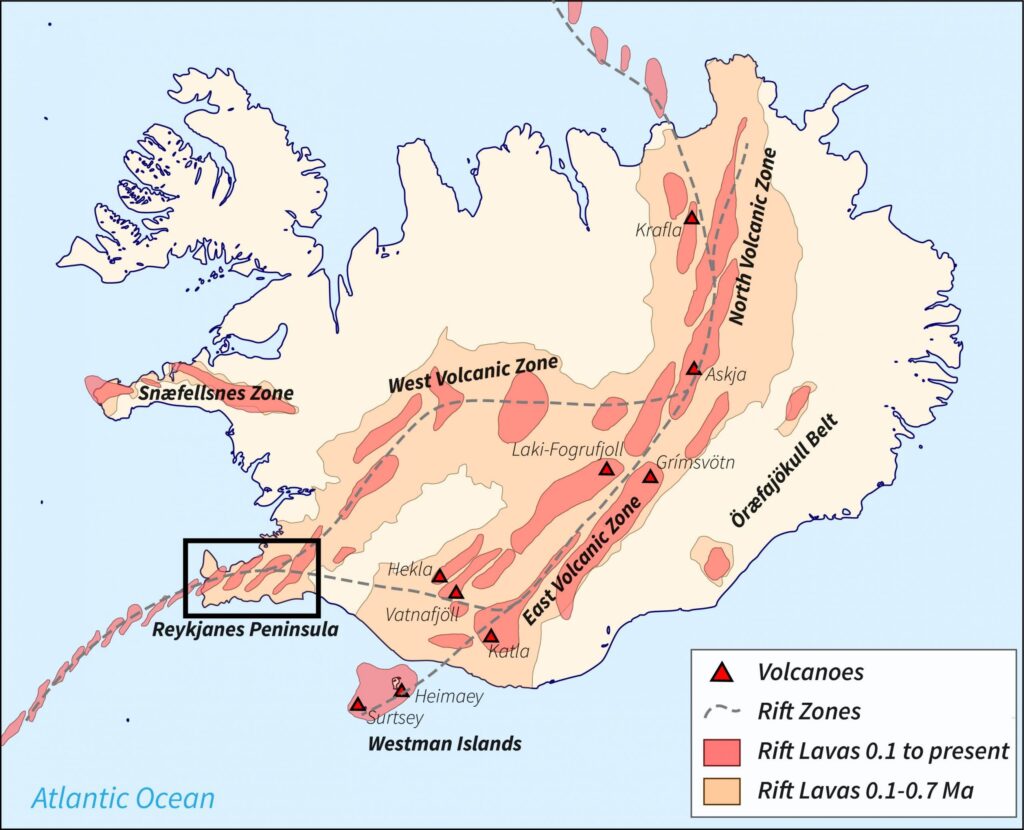
120nm of closed airspace around BIKF/Keflavik airport (remember, the volcano is just up the road) would look something like this:
There’s also a thing called the Volcanic Ash Contingency Plan that ICAO put together. This doc is the one you want to read – there are a few more scattered around online, but they’re all older versions of this one.

Where was ICAO when the Westfold fell?
This doc sprang from the misery caused by the eruption in 2010, and aims to set out what actually happens if a big volcano erupts.
Essentially, it goes like this:
- Volcano erupts. There’s ash all over the place.
- Volcanic ash people issue a volcanic ash warning.
- Notam people issue a Notam.
- Pilots/Operators read the Notam and don’t fly into the ash. ATC help them.

All volcano walking tours are cancelled.
What should I do if I fly through ash?
Don’t fly through ash.
But if you do, then do this:
- Reduce thrust.
- Do a 180 degree turnback.
- Put masks on.
- Declare MAYDAY.
- Panic a bit as you do whatever emergency tasks you need to do.
- Divert somewhere pronto.
Or as it says in more official language in the Contingency Plan:

If I do fly through ash, how scary will it be?
Very scary. Don’t do it. Here’s a list of nightmarish things that will probably happen if you do:
- Smoke, fumes or dust may appear in the cockpit. Get those masks on.
- Engine malfunctions, stalls, over-temperature, thrust loss, engine failure.
- Reduced visibility due to the abrasive effects of ash on windshields and landing lights.
- Pitot tubes may become blocked, so airspeed indications may become unreliable.
Advice: disconnect the autopilot, set engine thrust to an appropriate value and maintain the aircraft’s pitch attitude manually. This will keep the aircraft at a safe speed, but will probably result in difficulty to maintain the assigned altitude. Increased separation is required (above and below).

Another thing that might happen – SPIDERS.
Advisories and Warnings
The London Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC) is responsible for issuing any ash advisories for this region. You can access those here.

Senior staff meeting at the London Volcanic Ash Advisory Center.
The current alert level is Orange. Verbatim, this means that the volcano is ‘exhibiting heightened unrest with increased likelihood of eruption; or that an eruption is underway with minor ash emission…’ Or in other words, it may be about to erupt.
If you’re not familiar with the volcanic alert scale, here’s how it works:
 All traffic crossing the NAT or operating over Western Europe right now should be keeping a close eye on this one.
All traffic crossing the NAT or operating over Western Europe right now should be keeping a close eye on this one.
What’s the latest at BIKF/Keflavik Airport?
We’ve had a couple of reports from members who have been through there recently. If you’ve got anything to add, please file a report at Airport Spy! For info from the airport, you can contact the local handlers at jetcenter@icelandair.is or ops@southair.is.
More on the topic:
- More: NAT Crossing after GPS spoofing: a guide
- More: NAT Doc 007 – New Edition
- More: Don’t Climb! A Big NAT No-No
- More: Oceanic Clearance Removal mess – Version 4!
- More: NAT Clearance changes – a game! (V4)
More reading:
- Latest: Teterboro: RIP the RUUDY SIX
- Latest: 400% increase in GPS Spoofing; Workgroup established
- Latest: GPS Spoofing WorkGroup 2024
- Safe Airspace: Risk Database
- Weekly Ops Bulletin: Subscribe
- Membership plans: Why join OPSGROUP?











 Get the famous weekly
Get the famous weekly 






An eruption started tonight at 2217 UTC at the forecasted site, about 12nm southeast of BIKF. BIKF did close for about an hour, then reopened and is still open. So far there has been no ash plume, but fizzure and gases are flowing fast. Scientists are monitoring the sitation. Air traffic is at the moment expected to continue normally in and out of BIKF and BIRK.
It’s worth noting that if an eruption starts, which is considered imminent, the airspace within a 120nm radius from the eruption site will immediately close, until it can be confirmed that there is no ash plume in the case of fissure eruption with only lava and gasses, which is the most likely scenario with an eruption on land in that particular area. Scientists claim that there is a 15km long line southwest to northeast where magma is flowing and moving towards the surface. It could erupt anywhere close to that line. The most southern part of that line is under water. Should it erupt under water would be a different story with the associated ash plume into the atmosphere.
Information for the Icelandic Met Office can be found here: http://www.vedur.is