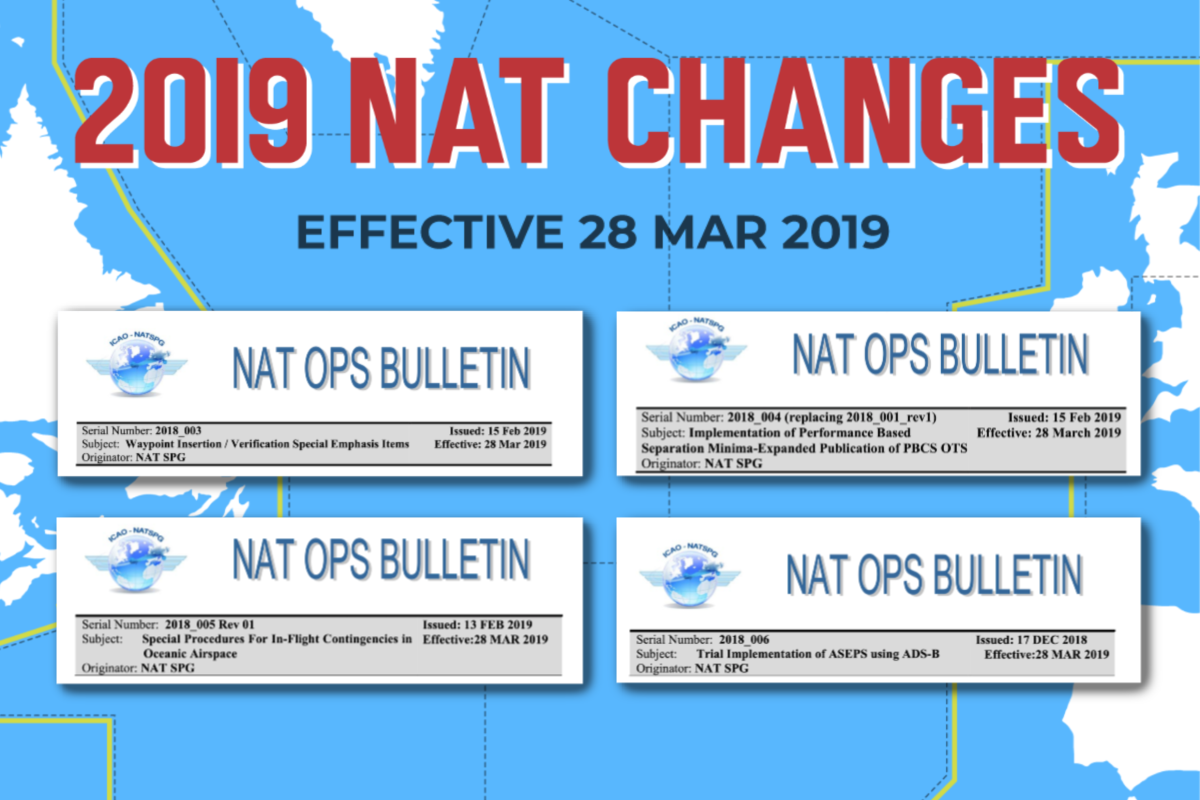
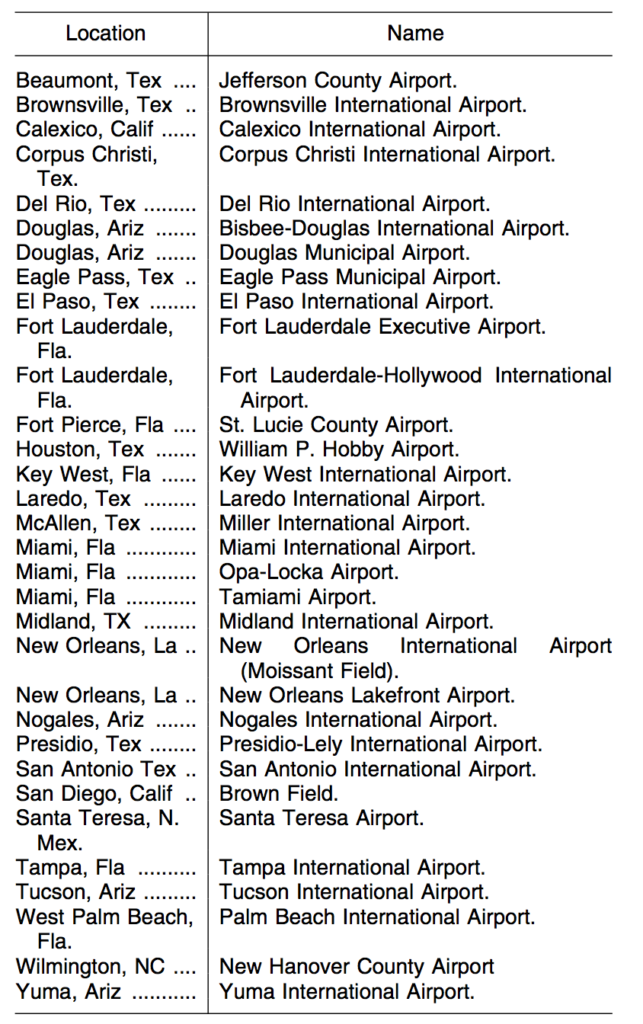
Starting 28th March 2019, there will be some changes to the contingency and weather deviation procedures on the NAT. ICAO has published a new NAT Ops Bulletin with all the details.
Before, there was a lot of confusion around the wording of these two procedures – but ICAO has now made this much clearer, and they have even included a little graphic to help us understand how it will work.
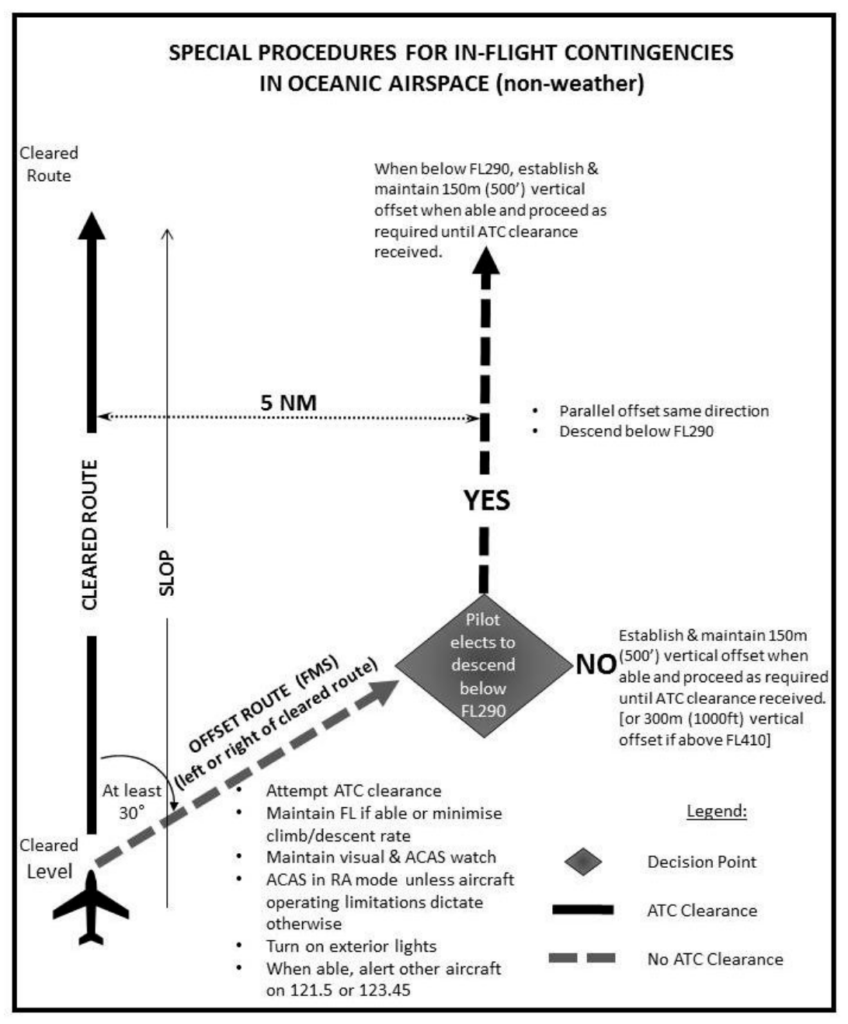
Thing is, it’s still a little clunky. So we decided to make our own version!
What’s new?
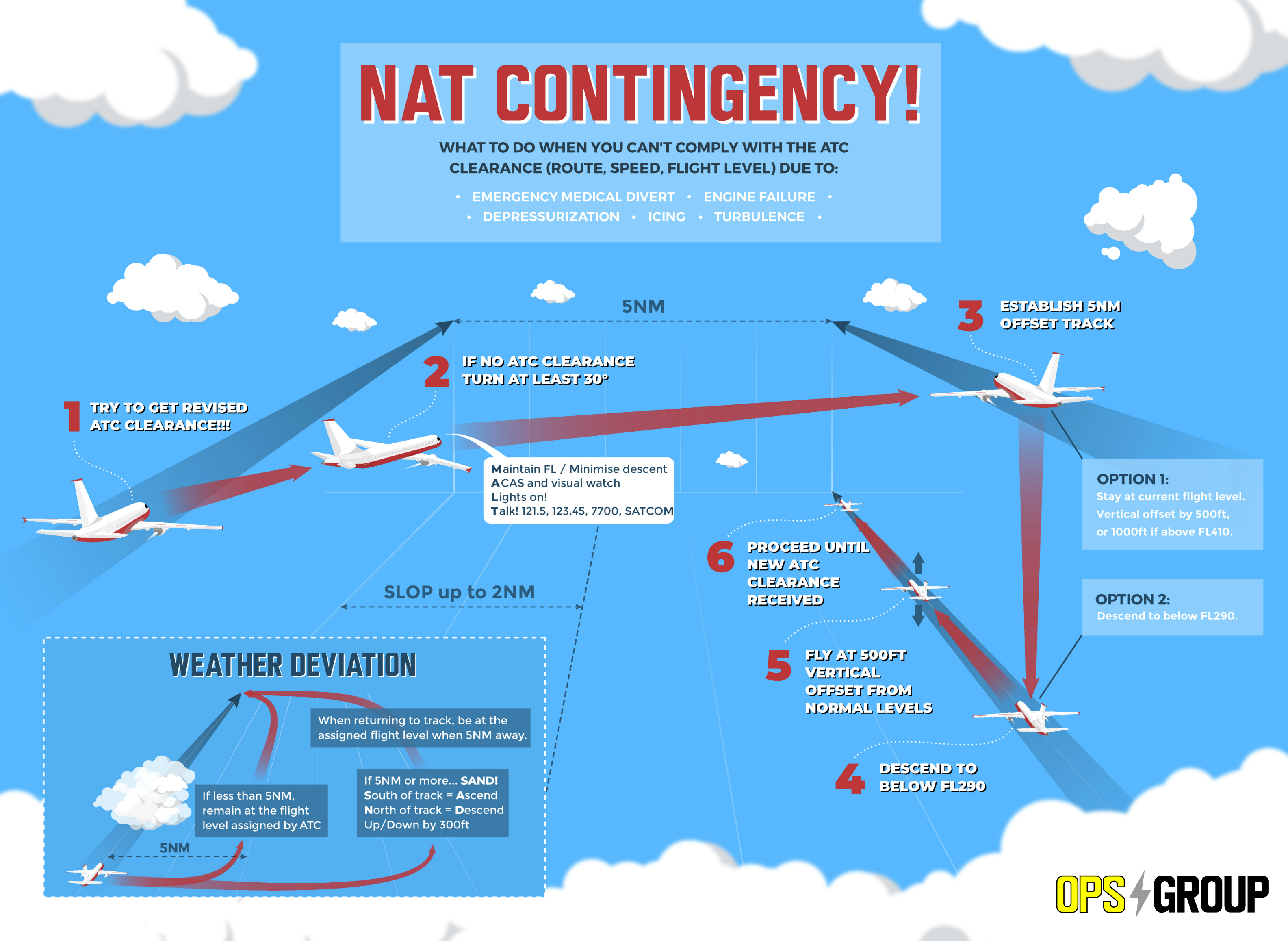
The simple answer is this: contingency offsets that previously were 15 NM with actions at 10 NM are basically now all 5 NM offsets with a turn of at least 30 degrees (not 45 degrees).
Rarely do we see ICAO oceanic contingency procedures undergo a formal revision. The last time a major revision occurred was in 2006 when ICAO standardized a 15 NM offset executed with a turn of at least 45 degrees. Prior to that, the North Atlantic and the Pacific had used different offset distances and a 90 degree turn.
Where and when?
A trial implementation is scheduled to begin in the NAT Region and New York Oceanic West starting 28th March 2019. ICAO is expected to formally publish the Standard in an update to PANS-ATM (ICAO Doc 4444) on 5 November 2020.
Why?
To support reduced separation being implemented in conjunction with Advanced Surveillance Enhanced Separation (ASEPS), Space Based ADS-B surveillance. The details for the ASEP trial can be found in NAT OPS Bulletin 2018-006 Trial Implementation of ASEPS using ADS-B.
Old version vs New version – full wording
Here’s the old version, as per the latest version of the NAT Doc 007, paragraph 13.3. (Note – this will be valid UNTIL 27 March 2019):
The aircraft should leave its assigned route or track by initially turning at least 45° to the right or left whenever this is feasible.
An aircraft that is able to maintain its assigned flight level, after deviating 10 NM from its original cleared track centreline and therefore laterally clear of any potentially conflicting traffic above or below following the same track, should:
a) climb or descend 1000 ft if above FL410
b) climb or descend 500 ft when below FL410
c) climb 1000 ft or descend 500 ft if at FL410
An aircraft that is unable to maintain its assigned flight level (e.g due to power loss, pressurization problems, freezing fuel, etc.) should, whenever possible, initially minimise its rate of descent when leaving its original track centreline and then when expected to be clear of any possible traffic following the same track at lower levels and while subsequently maintaining a same direction 15 NM offset track, descend to an operationally feasible flight level, which differs from those normally used by 500 ft if below (or by 1000 ft if above FL410).
Before commencing any diversion across the flow of adjacent traffic or before initiating any turn-back (180°), aircraft should, while subsequently maintaining a same direction 15 NM offset track, expedite climb above or descent below the vast majority of NAT traffic (i.e. to a level above FL410 or below FL290), and then maintain a flight level which differs from those normally used: by 1000 ft if above FL410, or by 500 ft if below FL410. However, if the flight crew is unable or unwilling to carry out a major climb or descent, then any diversion or turn-back manoeuvre should be carried out at a level 500 ft different from those in use within the NAT HLA, until a new ATC clearance is obtained.
And here’s the new version, as per the NAT OPS Bulletin 2018-005 Special Procedures for In-flight Contingencies in Oceanic Airspace (Note – this will be valid FROM 28 March 2019):
If prior clearance cannot be obtained, the following contingency procedures should be employed until a revised clearance is received:
Leave the cleared route or track by initially turning at least 30 degrees to the right or to the left, in order to intercept and maintain a parallel, direction track or route offset 9.3 km (5.0 NM).
Once established on a parallel, same direction track or route offset by 9.3 km (5.0 NM), either:
a) descend below FL 290, and establish a 150 m (500 ft) vertical offset from those flight levels normally used, and proceed as required by the operational situation or if an ATC clearance has been obtained, proceed in accordance with the clearance; or
b) establish a 150 m (500 ft) vertical offset (or 300 m (1000 ft) vertical offset if above FL 410) from those flight levels normally used, and proceed as required by the operational situation, or if an ATC clearance has been obtained, proceed in accordance with the clearance.
Note. — Descent below FL 290 is considered particularly applicable to operations where there is a predominant traffic flow (e.g. east-west) or parallel track system where the aircraft’s diversion path will likely cross adjacent tracks or routes. A descent below FL 290 can decrease the likelihood of: conflict with other aircraft, ACAS RA events and delays in obtaining a revised ATC clearance.
So to reiterate, the important change is that contingency offsets that previously were 15 NM with actions at 10 NM are basically now all 5 NM offsets with a turn of at least 30 degrees (not 45 degrees).
Weather deviations
If you have to deviate from your assigned track due to anything weather-related, there’s a whole different procedure to follow. Again, the NAT Ops Bulletin has all the details for this, but the bottom line seems to be:
For deviations of less than 5 NM, remain at the flight level assigned by ATC.
For deviations of 5 NM or more, when you are at the 5 NM point initiate a change as follows:
If flying EAST, descend left by 300ft, or climb right by 300ft.
If flying WEST, climb left by 300ft, or descend right by 300ft.
In other words – SAND! (South of track = Ascend, North of track = Descend; Up/Down by 300ft)
But remember, going right is probably better – it gets you out of the way of all the SLOP offset traffic that might be coming at you from the opposite direction!
Turnback procedure
In both the NAT Ops Bulletin and the new NAT Doc 007 which will take effect from 28 Mar 2019, ICAO has left out any specific reference to how to divert across the flow of traffic or turn-back procedure, and instead simplified it to just “proceed as required by the operational situation”. Turning back would assume you either employ the 5NM offset as per the new contingency procedure, or else get a new revised clearance.
Bottom line
If you operate in the NAT HLA, we recommend you read and review the NAT Ops Bulletin in its entirety. It’s relatively short but, beginning 28 March 2019, the procedures are expected to be implemented. You might want to prepare changes for your Ops Manuals and checklists too.
Make sure you stay tuned to OPSGROUP for changes that may occur as we approach 28 March 2019!
Further reading:
- On Nov 1st we had a call with 140 OPSGROUP members about upcoming changes on the NAT in 2019, and how we can effect change. OPSGROUP members can find the PDF notes of this in your Dashboard.
- A big thing driving the ASEPS trial is the rollout of Space-based ADS-B, which is scheduled to complete its deployment by 30 Dec 2018, giving us worldwide, pole-to-pole surveillance of aircraft. For more on that, and how it will affect operations on the NAT specifically, read the article by Mitch Launius here.
- Use our quick guide to figure out where you are welcome on the NAT, depending on what equipment and training you have.