Earlier this year, EASA withdrew its CZIBs (Conflict Zone Information Bulletins) for Israel and Iran, citing de-escalation. At the time, we wrote that the move seemed premature.
Then in June, the region saw one of its worst escalations in decades, with Israel and Iran trading missile strikes, the US and Gulf states scrambling to protect airbases, and most of the Middle East airspace system grinding to a halt.
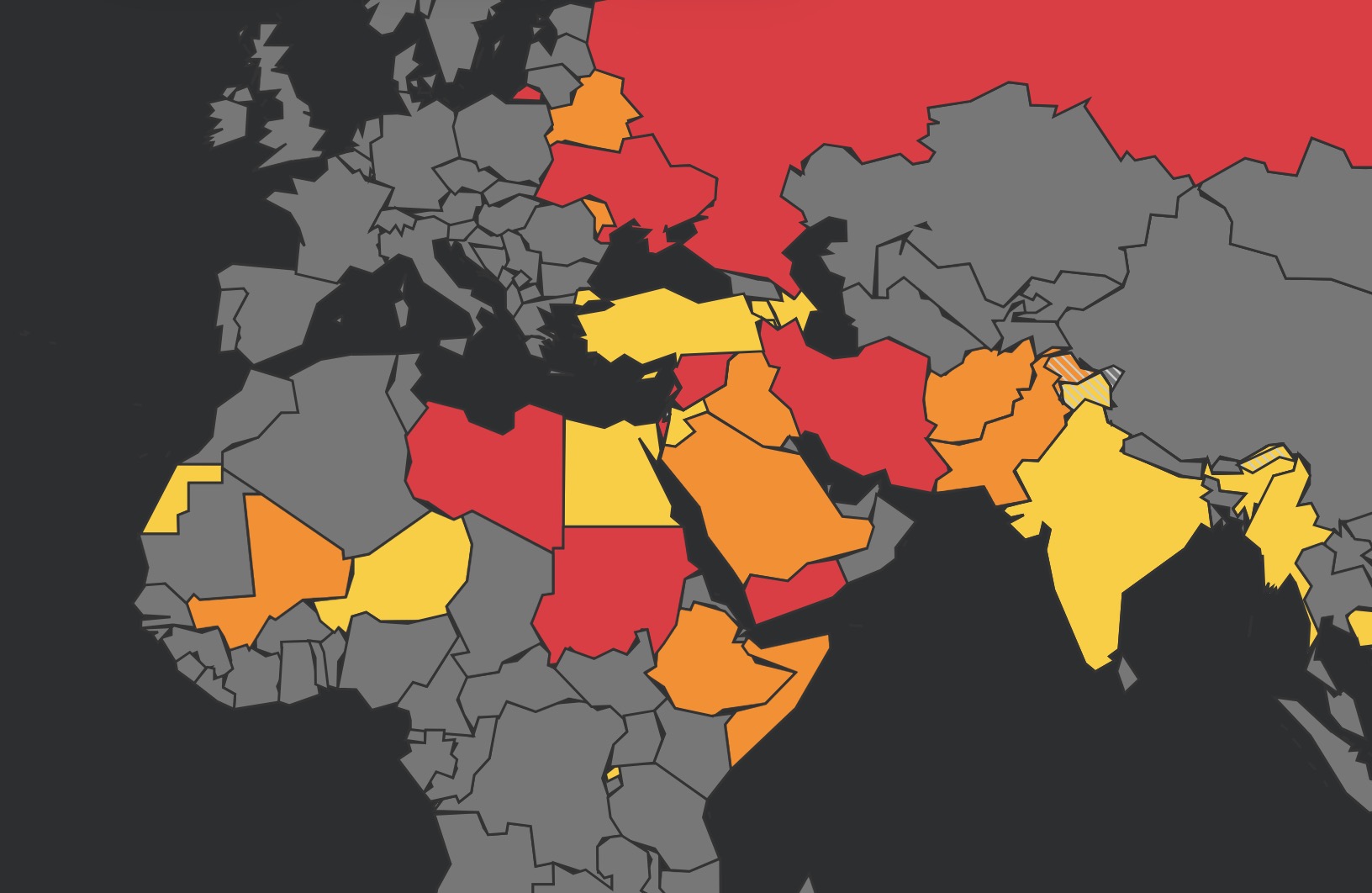
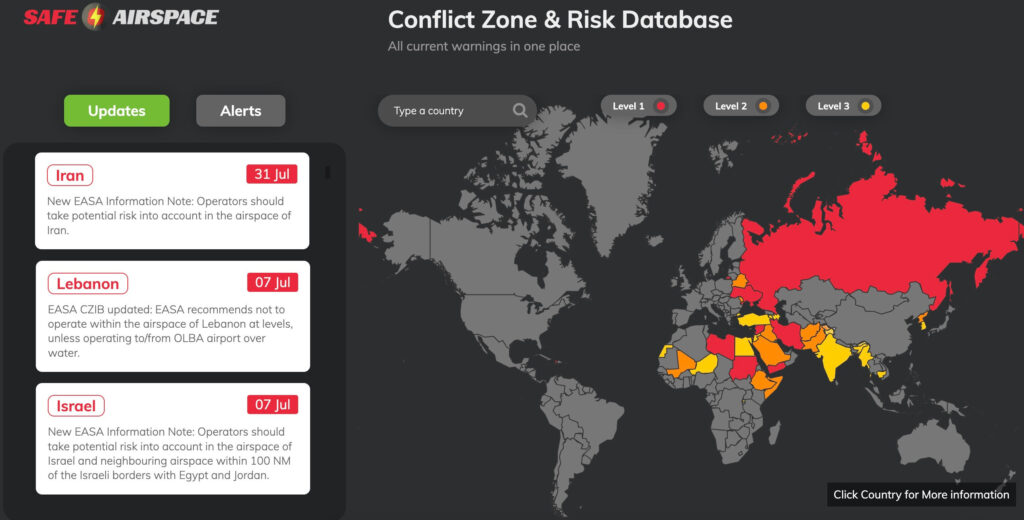
EASA responded by reissuing updated CZIBs advising operators to stay well clear of Iran, Iraq, Israel, Jordan, and Lebanon. They also flagged the risk of spillover into parts of Egypt and Saudi Arabia.
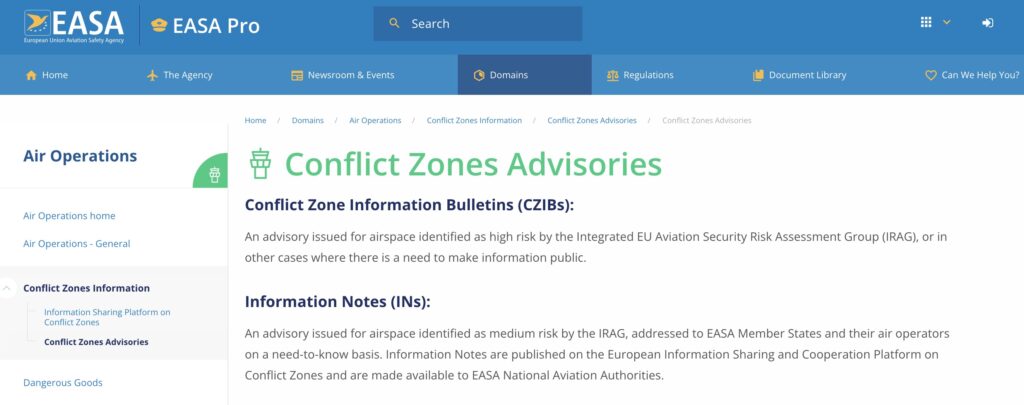
Now, just weeks after that guidance, those CZIBs have been withdrawn again. And once again, they’ve been replaced by vague and inaccessible “Information Notes” — only available to EU-based commercial operators, civil aviation authorities, and EU agencies. Everyone else (mainly biz jets and non-EU carriers) is locked out.
What’s changed?
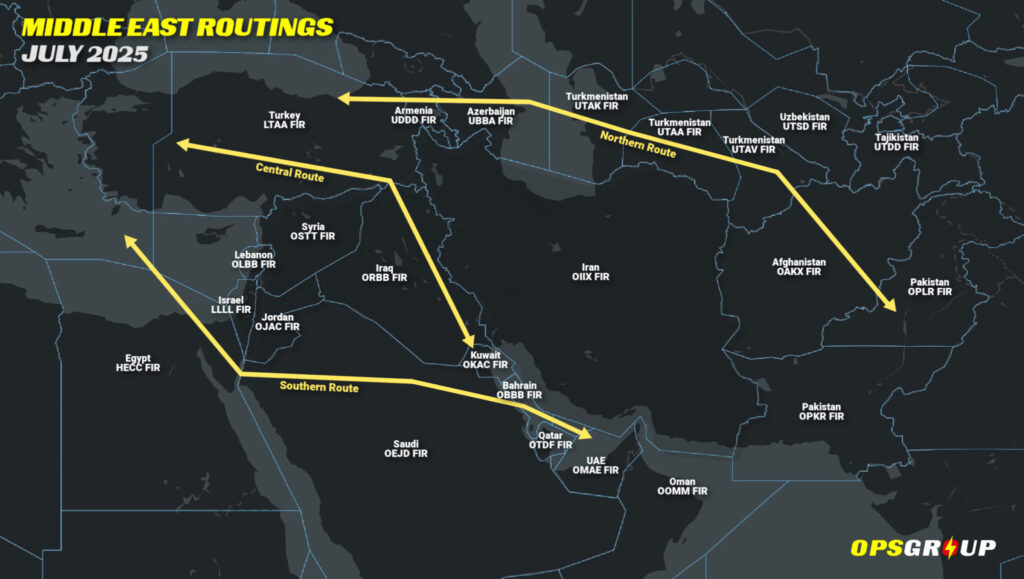
To recap: Following a ceasefire in early July, most FIRs across the region reopened. Iran reopened its OIIX/Tehran FIR in stages — first the east, then limited use of the west, and finally full ops. Israel began accepting traffic to LLBG/Tel Aviv on specific routings. Iraq reopened its airspace. Syria and Lebanon reopened too, albeit amid some brief re-closures. OPSGROUP members can access a full briefing here.
But the risks haven’t vanished. Most carriers are still avoiding direct routings over Iran. GPS spoofing remains widespread. FIRs across the region are fragile — especially the corridor between Israel and Iran, which could close again at short notice if the conflict resumes.
The CZIBs are gone, again.
EASA’s logic for removing them now appears to mirror their reasoning back in January — improving conditions, a reduction in active hostilities, and a belief that risk has subsided enough to no longer warrant a public advisory.
But here’s the key problem: the new “Information Notes” replacing CZIBs are not public. Unless you’re part of the inner circle of EU-based airlines or national regulators, you don’t get to see them. And the publicly accessible version doesn’t contain any detailed analysis, routing recommendations, or clarity on thresholds for escalation.
CZIBs were never binding, but they were visible — offering a common European position on conflict zone risk. The shift to restricted-access notes marks a change in how EASA communicates that risk.
A continuing need for caution
The removal of CZIBs shouldn’t be interpreted as an all-clear. The ceasefire between Israel and Iran remains fragile. Regional tensions persist. GPS interference continues to impact operations across the eastern Mediterranean and Persian Gulf. Routes through Athens and Nicosia FIRs remain congested as many operators still choose to avoid overflights of Iran and Israel altogether.
EASA’s risk assessments will of course evolve as the situation does — but for operators outside the EU system, the reduced visibility makes it more important than ever to consult a variety of sources: state-level airspace warnings, Notams, real-time airspace activity, and third-party guidance.
We maintain a full database of state issued airspace warnings at SafeAirspace.net, freely accessible to everyone.
The bottom line
While EASA’s decision to withdraw its CZIBs reflects improved conditions in parts of the region, the underlying risks remain dynamic. Operators should continue to treat Middle East operations with care — especially in and around Iran and Israel — and stay alert to changes that could result in rapid airspace restrictions or closures.
In short: just because EASA has stopped talking about it doesn’t mean the threat has gone away.
More on the topic:
- More: Crisis in Iran: Elevated Airspace Risk
- More: Ops to Europe: How to Get a Third Country Operator (TCO) Approval
- More: West Africa Ops: Routing Options and Restrictions
- More: Why EASA has Withdrawn Airspace Warnings for Iran and Israel
- More: Russia: Aircraft Shot Down, New EASA Airspace Warning
More reading:
- Latest: EU-LISA: The BizAv Guide
- Latest: Crisis in Iran: Elevated Airspace Risk
- Latest: Greece Winter Runway Closures
- Safe Airspace: Risk Database
- Weekly Ops Bulletin: Subscribe
- Membership plans: Why join OPSGROUP?










 Get the famous weekly
Get the famous weekly 





