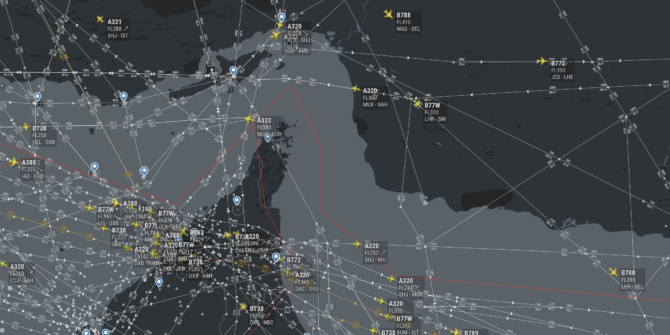
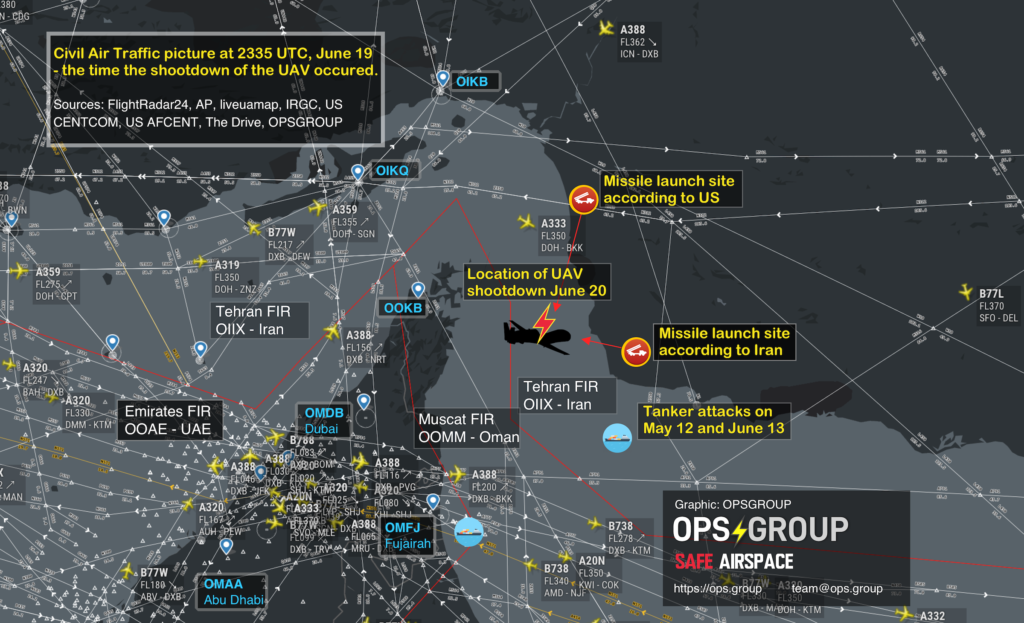
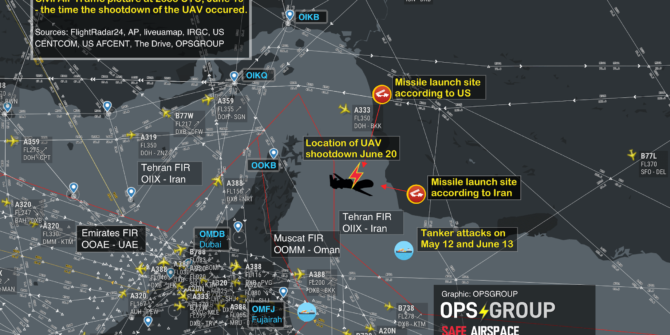
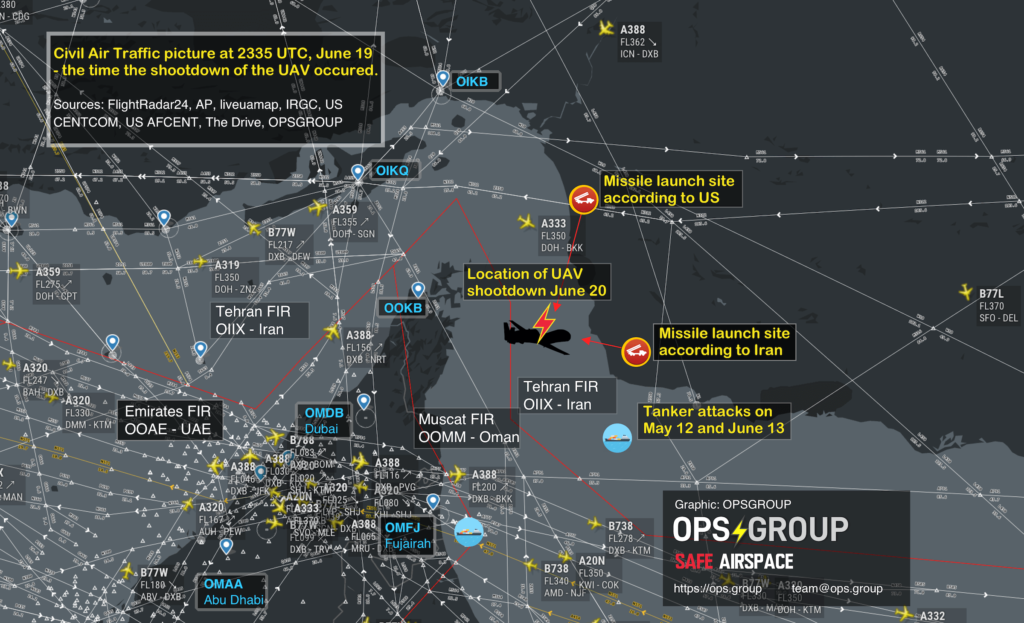
The FAA has issued an Emergency Order to US Civil Aircraft, prohibiting all American aircraft operators from entering the Tehran Flight Information Region (OIIX) FIR in the area above the Persian Gulf and Gulf of Oman.
Notam A0019/19 was issued at 0148 UTC, June 21st.
The Notam specifically prohibits any airline or aircraft operator from flying within Iranian airspace in the region that the US drone was shot down in on June 20th.
Some airlines had already reported suspending operations in Iranian airspace. This Notam ensures that US operators cannot operate in the area. Although the official applicability is to US aircraft only, since MH17 all countries rely on advice from the US, the UK, France and Germany to highlight airspace risk.
The full Notam follows (bolded parts by OPSGROUP):
A0019/19 NOTAMN Q) KICZ/QRDLP/IV/NBO/AE/000/999/
A) KICZ PART 1 OF 2
B) 1906210148
C) PERM
E) SECURITY..UNITED STATES OF AMERICA PROHIBITION AGAINST CERTAIN FLIGHTS IN THE OVERWATER AREA OF THE TEHRAN FLIGHT INFORMATION REGION (FIR) (OIIX) ABOVE THE PERSIAN GULF AND GULF OF OMAN ONLY.
ALL FLIGHT OPERATIONS IN THE OVERWATER AREA OF THE TEHRAN FLIGHT INFORMATION REGION (FIR) (OIIX) ABOVE THE PERSIAN GULF AND GULF OF OMAN ONLY ARE PROHIBITED UNTIL FURTHER NOTICE DUE TO HEIGHTENED MILITARY ACTIVITIES AND INCREASED POLITICAL TENSIONS IN THE REGION, WHICH PRESENT AN INADVERTENT RISK TO U.S. CIVIL AVIATION OPERATIONS AND POTENTIAL FOR MISCALCULATION OR MIS-IDENTIFICATION.THE RISK TO U.S. CIVIL AVIATION IS DEMONSTRATED BY THE IRANIAN SURFACE-TO-AIR MISSILE SHOOT DOWN OF A U.S. UNMANNED AIRCRAFT SYSTEM ON 19 JUNE 2019 WHILE IT WAS OPERATING IN THE VICINITY OF CIVIL AIR ROUTES ABOVE THE GULF OF OMAN.
A. APPLICABILITY. THIS NOTAM APPLIES TO: ALL U.S. AIR CARRIERS AND COMMERCIAL OPERATORS; ALL PERSONS EXERCISING THE PRIVILEGES OF AN AIRMAN CERTIFICATE ISSUED BY THE FAA, EXCEPT SUCH PERSONS OPERATING U.S.-REGISTERED AIRCRAFT FOR A FOREIGN AIR CARRIER; AND ALL OPERATORS OF AIRCRAFT REGISTERED IN THE UNITED STATES, EXCEPT WHERE THE OPERATOR OF SUCH AIRCRAFT IS A FOREIGN AIR CARRIER.
B. PERMITTED OPERATIONS. THIS NOTAM DOES NOT PROHIBIT PERSONS DESCRIBED IN PARAGRAPH A (APPLICABILITY) FROM CONDUCTING FLIGHT OPERATIONS IN THE ABOVE NAMED AREA WHEN SUCH OPERATIONS ARE AUTHORIZED EITHER BY ANOTHER AGENCY OF THE UNITED STATES GOVERNMENT WITH THE APPROVAL OF THE FAA OR BY A DEVIATION, EXEMPTION, OR OTHER AUTHORIZATION ISSUED BY THE FAA ADMINISTRATOR. OPERATORS MUST CALL THE FAA WASHINGTON OPERATIONS CENTER AT 202-267-3333 TO INITIATE COORDINATION FOR FAA AUTHORIZATION TO CONDUCT OPERATIONS.
C. EMERGENCY SITUATIONS. IN AN EMERGENCY THAT REQUIRES IMMEDIATE DECISION AND ACTION FOR THE SAFETY OF THE FLIGHT, THE PILOT IN COMMAND OF AN AIRCRAFT MAY DEVIATE FROM THIS NOTAM TO THE EXTENT REQUIRED BY THAT EMERGENCY.
THIS NOTAM IS AN EMERGENCY ORDER ISSUED UNDER 49 USC 40113(A) AND 46105(C). ADDITIONAL INFORMATION IS PROVIDED AT: HTTPS://WWW.FAA.GOV/AIR_TRAFFIC/PUBLICATIONS/US_RESTRICTIONS/
Earlier today, we published an article summarizing the risk to Aircraft Operators in the Gulf region – “The Threat of a Civil Aircraft Shootdown in Southern Iran is Real”
In addition to the Notam, the FAA Threat Analysis Division have also published background information on the current situation (download that PDF here )
In that document, the FAA says: “Although the exact location of the attack is not yet available, there were numerous civil aviation aircraft operating in the area at the time of the intercept. According to flight tracking applications, the nearest civil aircraft was operating within approximately 45nm of the Global Hawk when it was targeted by the Iranian SAM. FAA remains concerned about the escalation of tension and military activity within close proximity to high volume civil air routes and the Iran’s willingness to use long-range SAMs in international airspace with little to no warning. As a result, there is concern about the potential for misidentification or miscalculation which could result in the inadvertent targeting of civil aviation.”
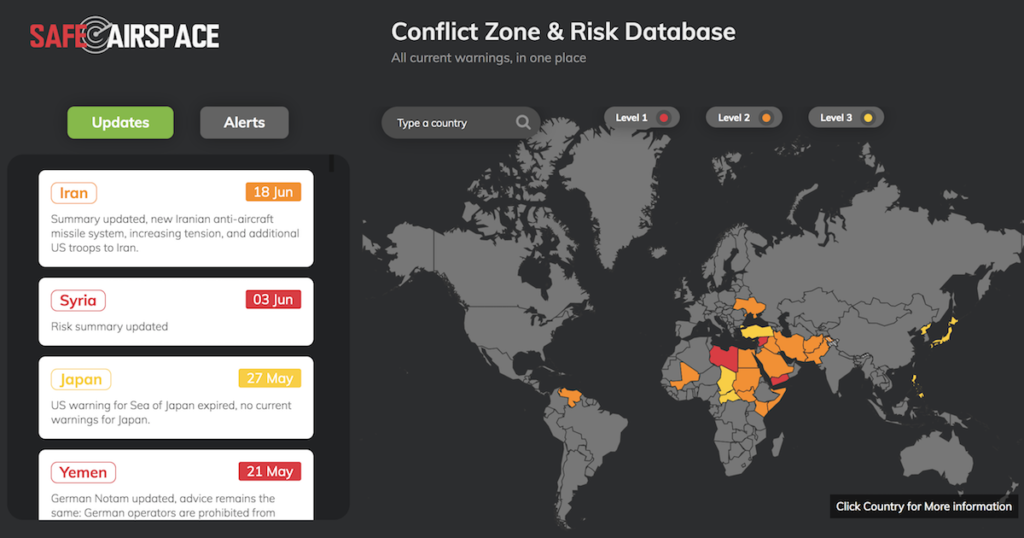
The Iran risk is being monitored at Safe Airspace – the Conflict Zone & Risk Database. The Iran country page also has more information on further overflight considerations in other parts of the Tehran FIR.