EASA has withdrawn their Iran CZIB, so what does this actually mean for the safety and security of air operations there?
What is an EASA CZIB?
First up, a CZIB is a Conflict Zone Information Bulletin (if you aren’t familiar with the term.)
These are put together by EASA based on aeronautical publications issued by worldwide states, and an assessment of the overall known risks and threats which EASA do via their Integrated EU Aviation Security Risk Assessment Group. Quite a mouthful. The point is they are sharing info on conflict zones to help operators do their own risk assessment on whether to head in there or not.
OK. So, when we take a look at EASA’s CZIBs they actually are more of a summary of references to other state and authority warnings. EASA CZIBs do not in themselves, appear to make an assessment of risk. They just share what everyone else says and contain a recommendation which more often than not goes something like this –
“Operators should take this information and any other relevant information into account in their own risk assessments, alongside any available guidance or directions from their national authority as appropriate.”
If you want to check out their active ones you can do so here.
EASA updated a large number of them in October 2021. 10 in fact, which included the likes of Iraq, Libya, Mali, Afghanistan, South Sudan… interestingly, they did not update their Iranian CZIB.
Instead, they withdrew it.
Why did they withdraw the Iranian CZIB?
That’s the big question.
Given that the EASA CZIBs do little more than summarise actual risk statements from other states, and considering other major states still have valid warnings for Iran, it does seem rather odd.
EASA have suggested their decision to withdraw this CZIB is based off an agreement from a recent meeting in which they decided that the situation in Iran has positively improved allowing to withdraw the current CZIB and to issue as replacement an Information Note shared within the European commercial aviation community on a ‘Need-to-know’ basis.
So, when EASA withdraws a CZIB, this does not mean individual states have also withdrawn their own warnings. We have not seen the ‘Information Note’.
All still valid
You can click below to read the (now withdrawn) EASA CZIB.
We think the risk remains.
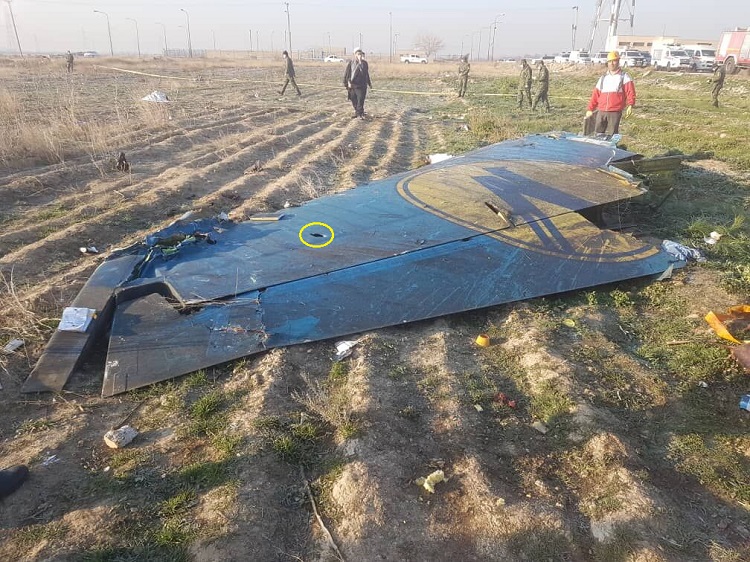
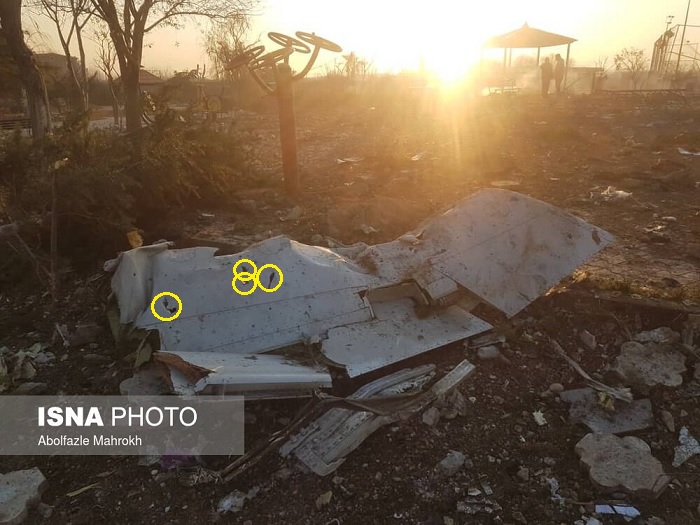
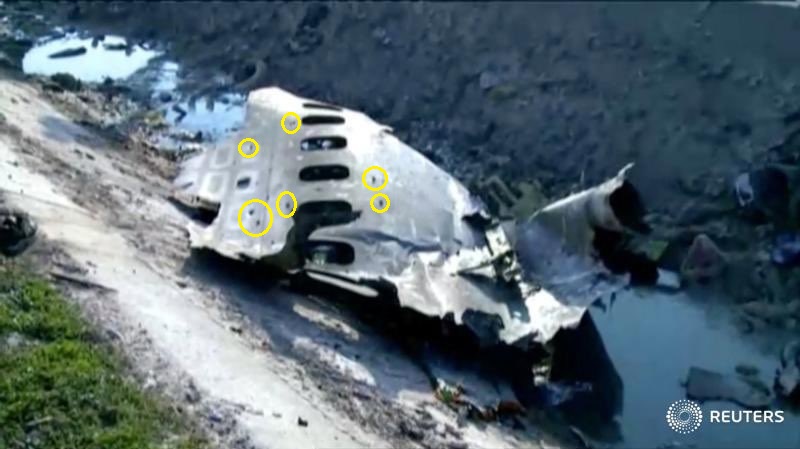
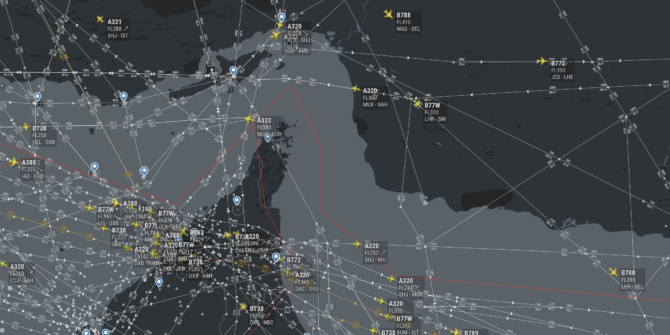
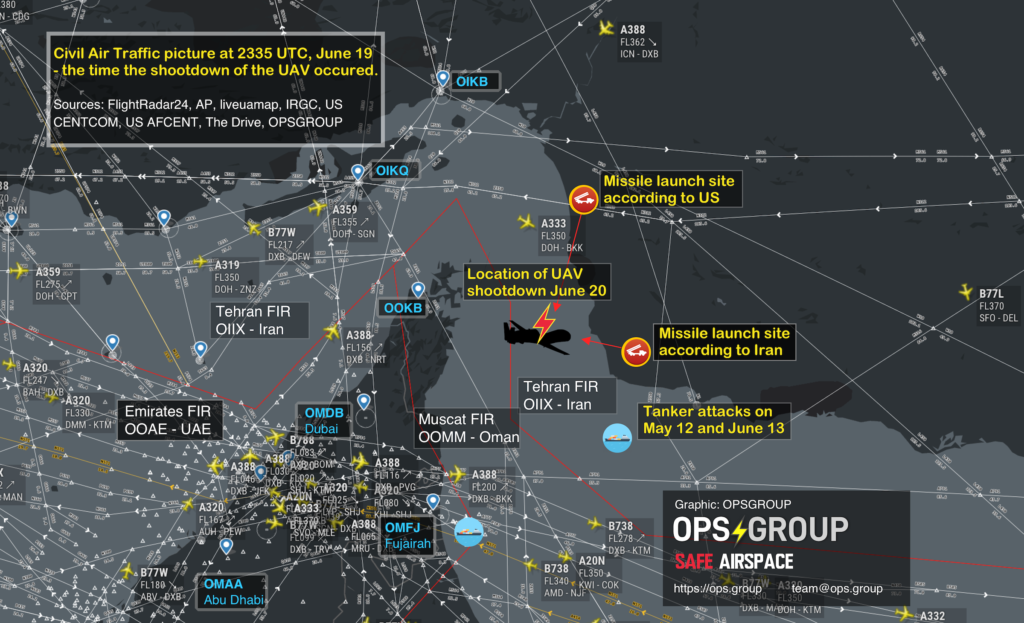
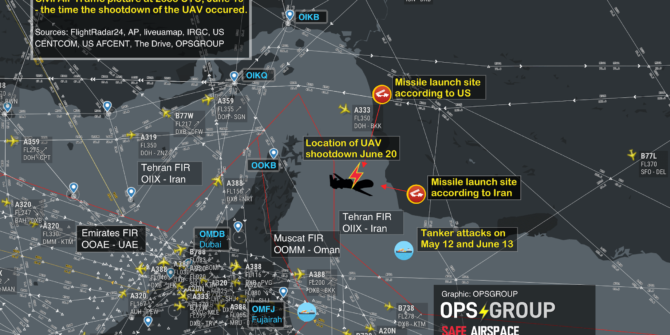
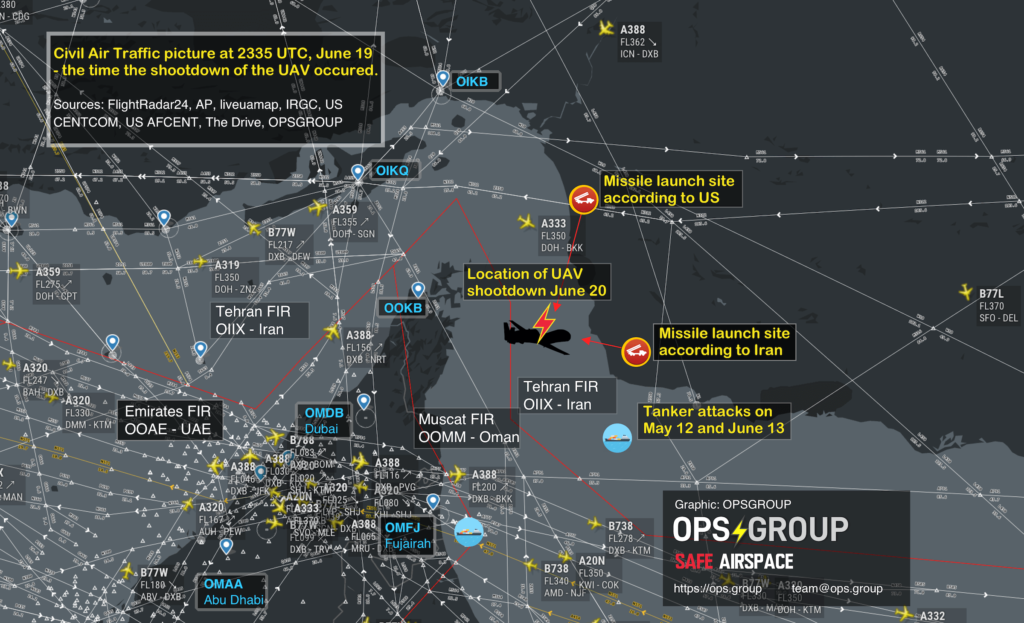
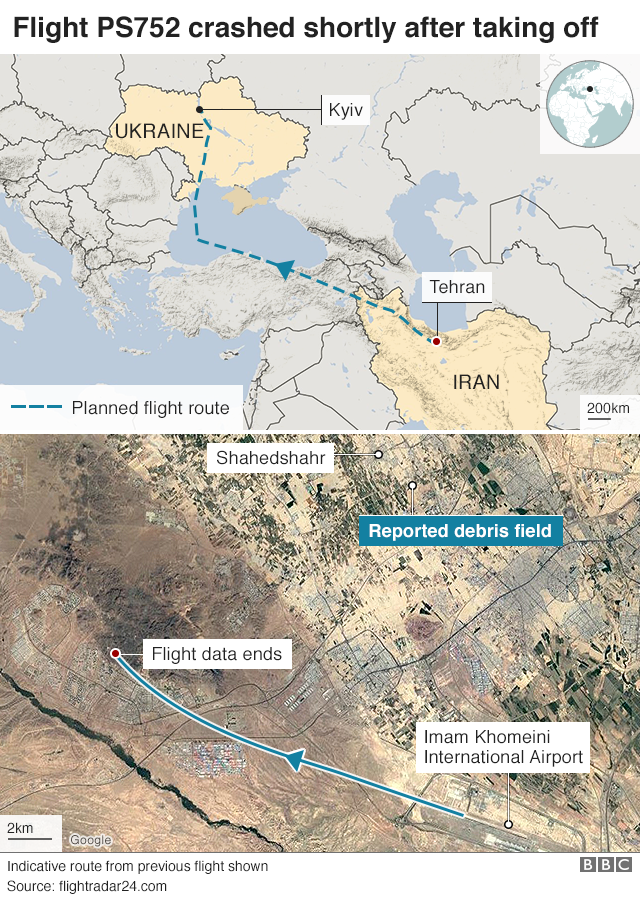
In 2020, Ukraine International Airlines flight PS752 was shot down in the vicinity of OIIE/Tehran, by the Iranian Air Defense system when it was misidentified. Iran possess significant anti-aircraft weaponry. This weaponry is in place due to ongoing conflict within Iran, and that has not changed.
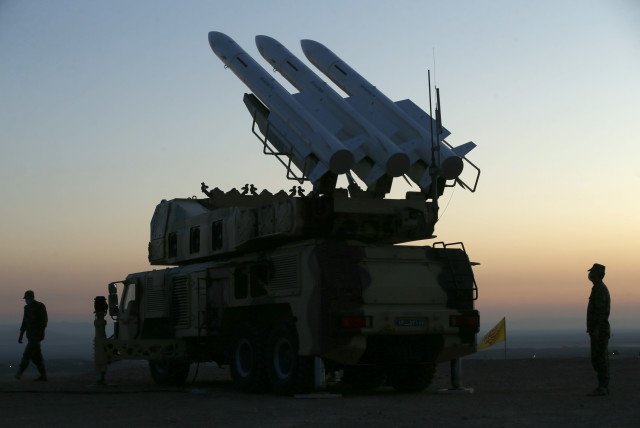

The Iranian ‘Air Dome’ Defense system
As with all risk, likelihood is dependant on capability (they have that), and intent.
Intent is an interesting one. The didn’t intend to shoot anyone down with their Air Defense systems, and they don’t usually fire their anti-aircraft weaponry without good reason, which means a risk of misidentification is far higher during times of active attack, when enemy forces are being targeted.
But the situation in Iran remains volatile, and so the risk level remains.
What is the risk?
A fair few airlines do overfly Iran. The ones that don’t generally have political reasons not too – this doesn’t mean the risk isn’t there. The political tensions between some countries and Iran mean the risk of being targeted or experiencing security threats on the ground is far higher.
If the state your aircraft is registered in is on relatively good political terms with Iran then overflying the country above a safe flight level poses less risk if you remain at that level.
Descend below FL260-ish and it is a different situation. And if you overfly anywhere, there is a chance you will need to descend and even divert in for certain emergencies. So your risk assessment when “just overflying” needs to take that into account.
Remember – just because you only want to overfly and don’t plan on going into Iran does not mean the risk does not apply to you. If there is a possibility you might have to divert in then the risk must be taken into account.
This is why operators who do fly into Iran generally have “TOD” checks – a SATCOM call, for example, to their company to confirm the security situation on the ground prior to heading in below that safe altitude. Basically, a check to ask if stuff is kicking off or not.
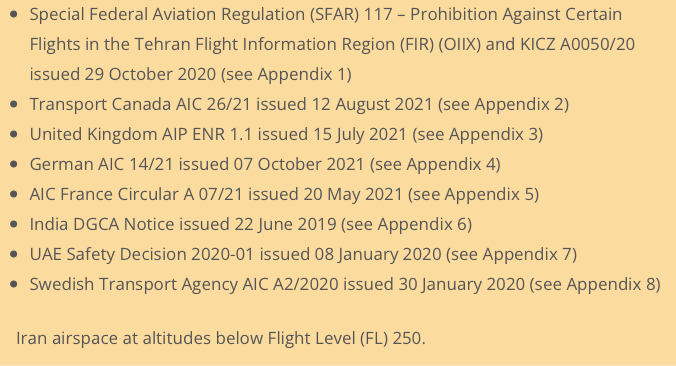
What do other states say?
The UK CAA Notam EGTT V0012/21 was issued in July 2021. This covers a “general” airspace security warning for a whole bunch of countries, including Iran, and suggests you go check the UK AIP En-route 1.1 section 1.4.5 for more info.
1.4.5 says there is a “potential risk to aviation overflying this area at less than 25,000ft” because of “dedicated anti-aviation weaponry”. France say don’t go below FL320. The US says don’t go at all.
The risk is still there, and that risk was actually summed up pretty well in the now withdrawn CZIB – “due to the hazardous security situation, and poor coordination between civil aviation and military operations, there is a risk of misidentification of civil aircraft.”
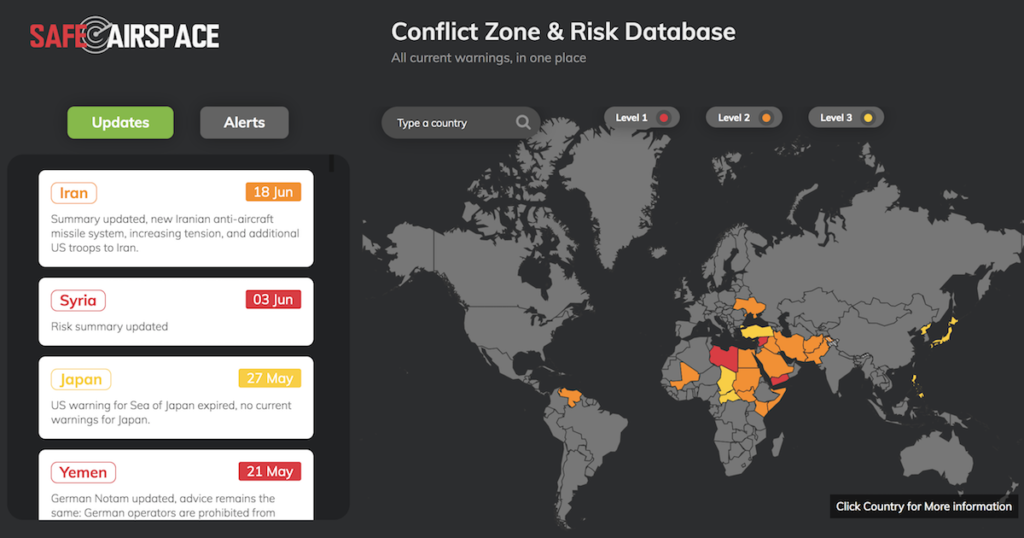
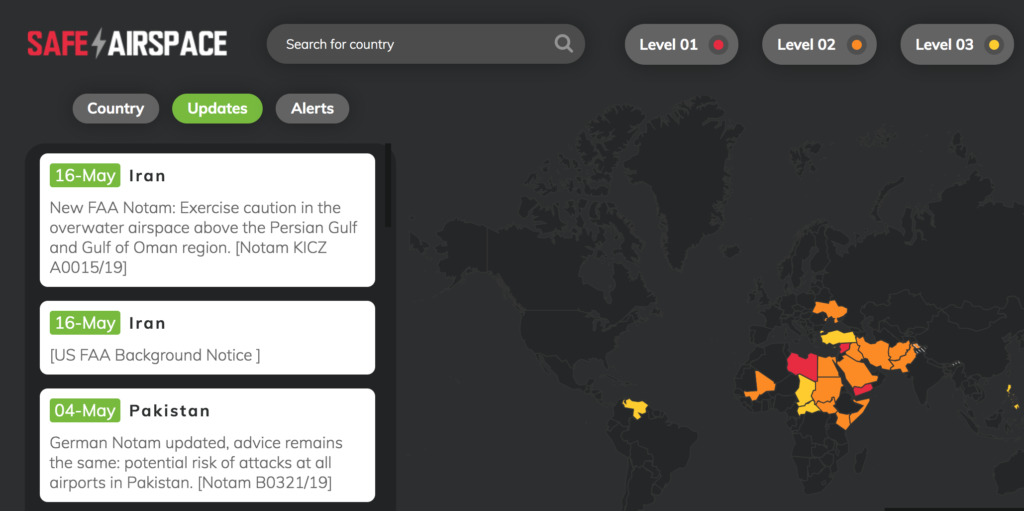
If you want a summary of all the current warnings and details, visit our Safeairspace page.
The current situation in Iran.
The situation is volatile. There is significant political conflict between Iran and some of their regional neighbours. There is also internal conflict. The primary risk remains the potential for misidentification from the air defence systems, or surface to surface missiles targeting rebels. There are secondary risks from ballistic missile tests (often tested without Notams) and GPS jamming.
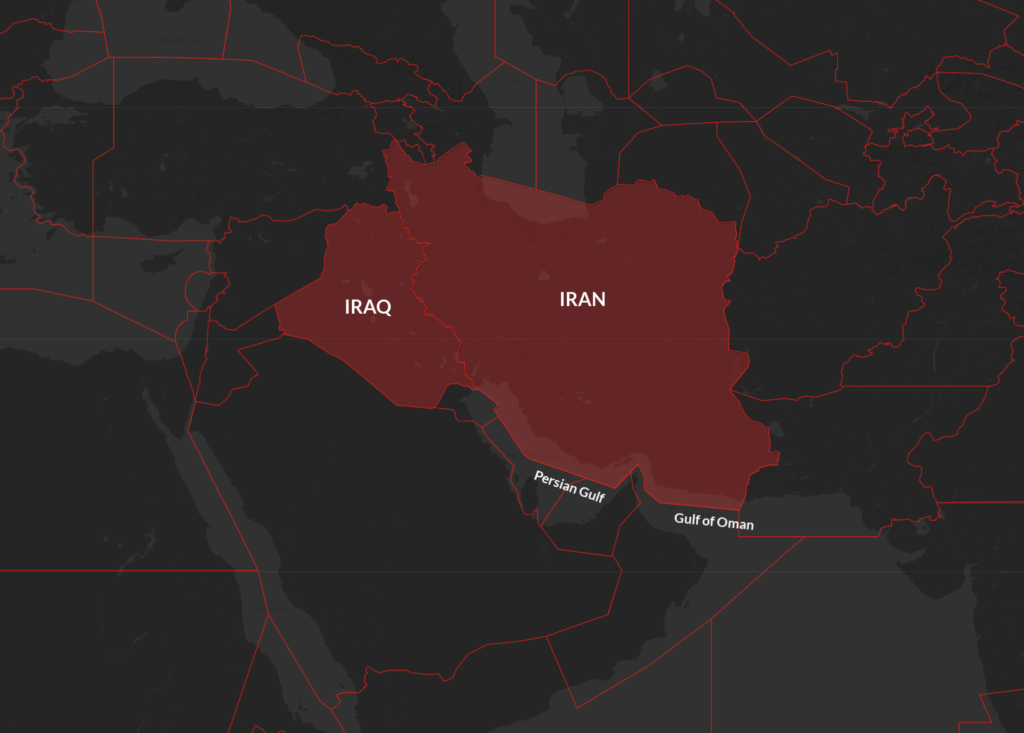
Both airspaces and the Persian Gulf pose an airspace risk.
Safeairspace Summary
Our view is that the removal of the EASA CZIB does not signify any change to the threat level in Iran. States have not removed their own warnings and so our Safeairspace warning remains the same until such time as further information is provided on how Iran have positively improved the situation.
Want a full briefing?
Just click here. SafeAirspace is our conflict zone and risk database run by OPSGROUP. We continually assesses the risk to operators the world over. It presents that information in a way that will always be simple, clear, and free. You can also sign up to our new fortnightly risk briefing that contains only what you need to know, simply by subscribing.




 Germany
Germany