You’re halfway across the Atlantic when ATC declares that they are suspending all services. TIBA procedures are now in effect. Would you know what to do next? As Covid infections impact ATC facilities, short notice closures are currently a constant risk. With the possibility of an entire oceanic ATC area being shut down due to Covid, there are some big questions to consider, and to factor in to your planning: Are you tankering enough fuel if you suddenly have to fly around large sections of oceanic airspace? Where are your ETPs? Do you have a wet footprint?
Back in 2011, there was an incident where transatlantic flights were not allowed to enter CYQX/Gander oceanic airspace due to a smoke situation in ATC control centre which meant that controllers had to be evacuated. They issued a Notam, but that wasn’t much use to the traffic en-route at the time, which all had to be re-routed around the CYQX/Gander Oceanic FIR – a vast portion of oceanic airspace.
![]() Fast forward to March of this year, where New York Air Route Traffic Control Center was forced to temporarily close due to a controller testing positive for Covid-19. The affected airspace restricted flights into New York area airports, with aircraft having to take longer routes in order to avoid closed sectors, as well as Oceanic airspace which stretches from New York past Bermuda and services flights heading to the Caribbean, Europe, South America, and Africa.
Fast forward to March of this year, where New York Air Route Traffic Control Center was forced to temporarily close due to a controller testing positive for Covid-19. The affected airspace restricted flights into New York area airports, with aircraft having to take longer routes in order to avoid closed sectors, as well as Oceanic airspace which stretches from New York past Bermuda and services flights heading to the Caribbean, Europe, South America, and Africa.
The New York ARTCC is not the only ATC center that has been affected over the past few months due to controllers coming down sick with coronavirus. Eleven sites across the US, including at major airports in New York, Chicago, and Las Vegas, have been temporarily closed for cleaning, affected flight operations. Some facilities have been closed for several days leaving inbound and departing aircraft left to their own devices for taxi, take-off, and landing.
NAT Doc 006 is the official go-to manual to check what happens during these “ATC Zero” events on the North Atlantic, but the spate of recent ATC shutdowns in the US led the FAA to re-examine the increased potential for these situations occurring during the Covid crisis, and in early July they published a SAFO as a result.
The NAT Doc 006 and the US SAFO are great resources, but here are two more which you might not know about!
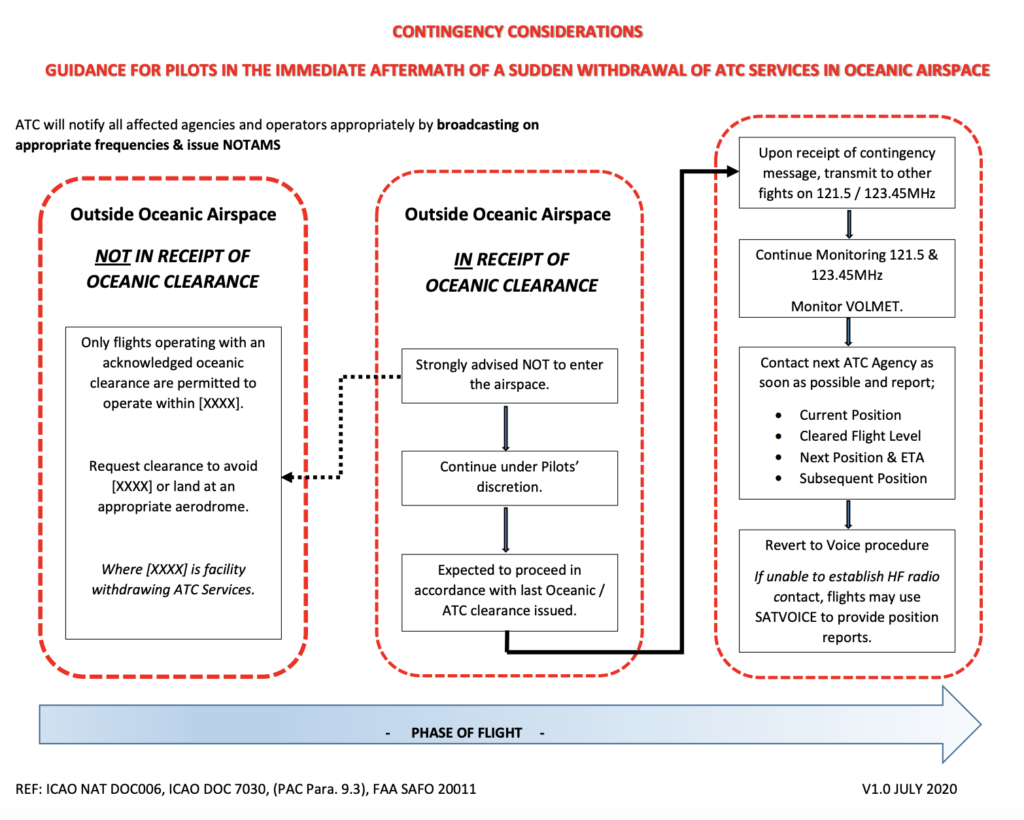
Code7700.com has published an excellent 2-page crib sheet with clear guidance for pilots on what to do in these situations. You can download it here:
 And 30WestIP.com have recorded a video webinar discussing this topic in more detail, which you can view here:
And 30WestIP.com have recorded a video webinar discussing this topic in more detail, which you can view here: