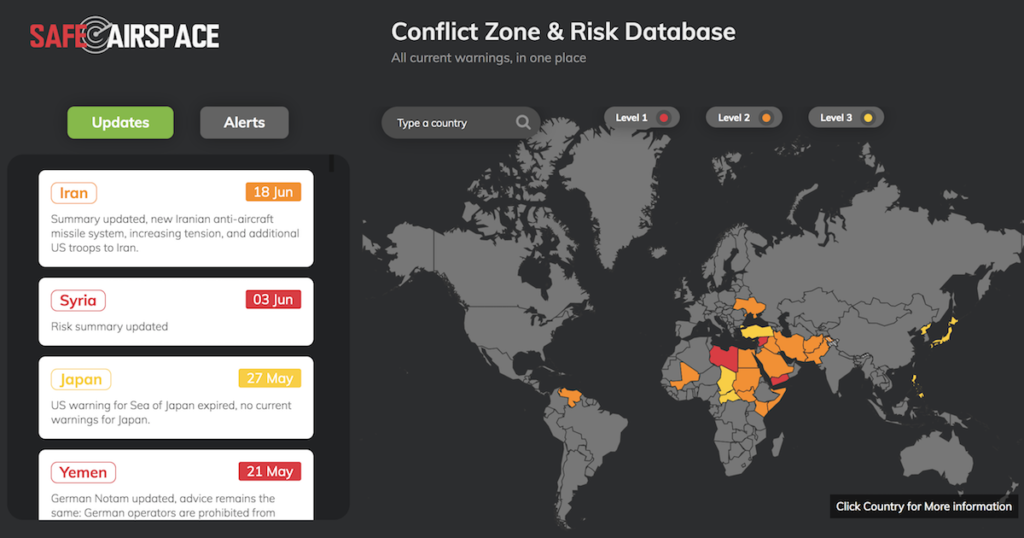
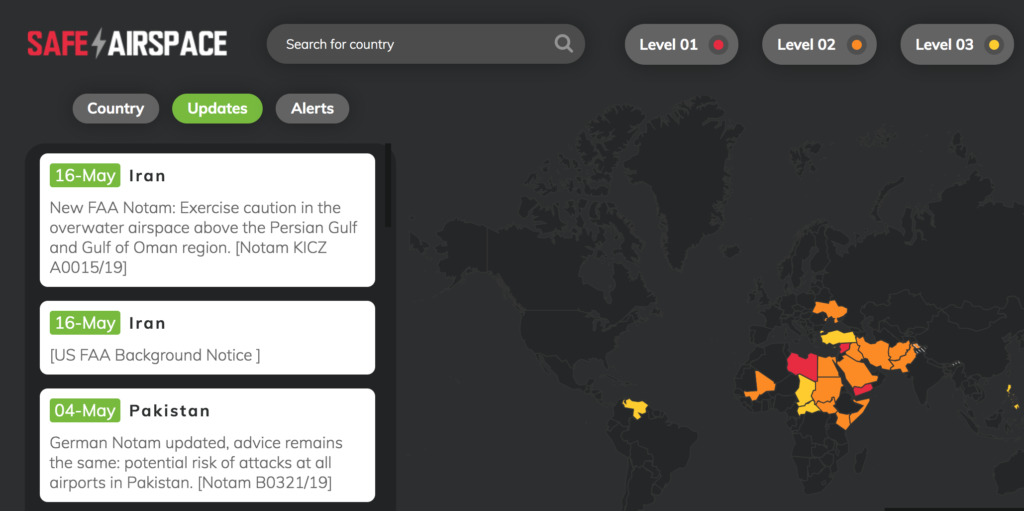
Our SafeAirspace website contains all the current airspace warnings from major authorities for various airspace regions around the world.
If you are a US registered operator, then you can find info on the FAA warnings here too.
But we thought we would make a brief summary for you here, just as a refresher on what the current KICZ status is for each country.
Where can I find them?
SafeAirspace pulls all the latest info from the US FAA’s dedicated webpage which contains all their ‘Prohibitions, Restrictions and Notices’. This is where you can find their International Security NOTAMs (KICZ) and Special Federal Aviation Regulations (SFAR), plus information relating to the background of the situations and the prohibitions/restrictions.
A summary
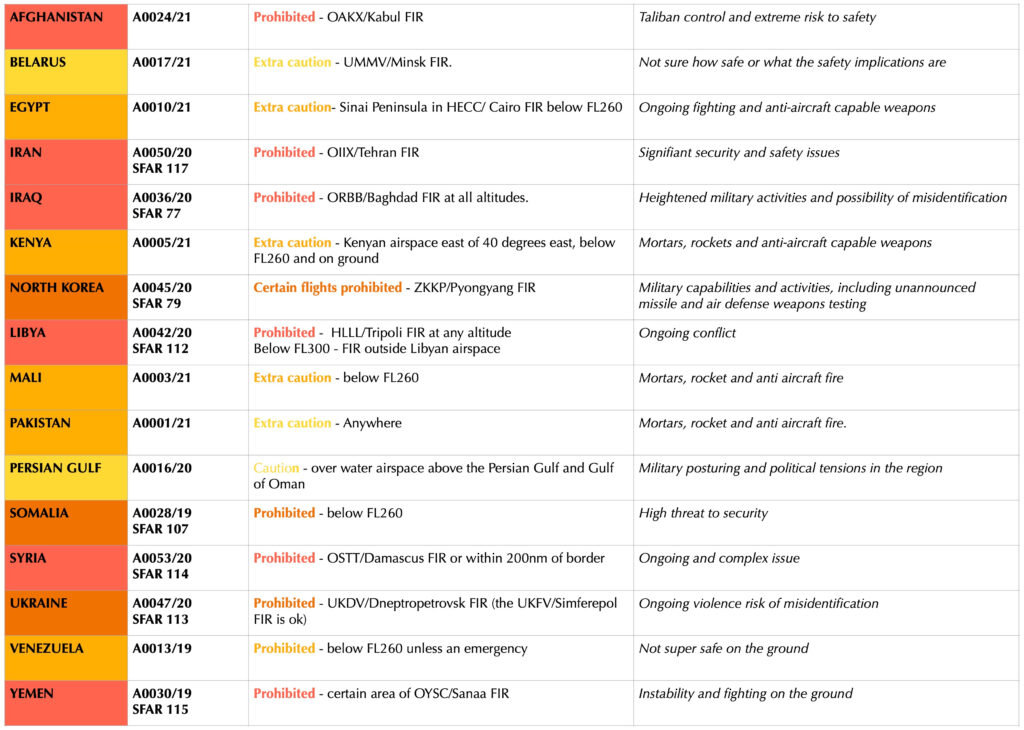
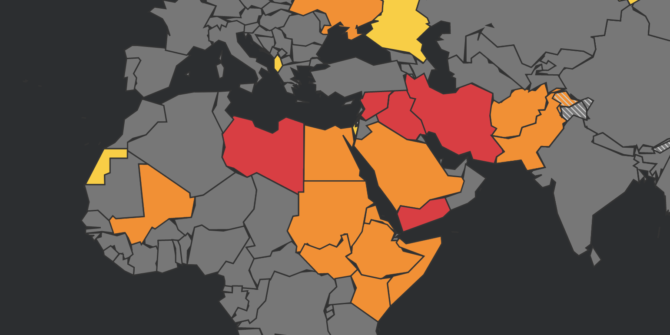
Here is a summary of the countries with a US FAA airspace prohibition/restriction in force, and what it (very briefly) says for each one.
Afghanistan
US Operators are prohibited from operating in the OAKX/Kabul FIR. Overflights are still allowed on airways P500 and G500 which run alongside the eastern boundary of the Kabul FIR.
Why? There is a risk of direct and indirect fire targeting airports and from surface-to-air fire targeting aircraft operating at low altitudes. Additionally, the recent Taliban takeover has led to zero ATC control across the entire airspace and an extreme threat to aircraft and crew safety and security on the ground. Air defense forces in all neighboring states are likely at high alert status within respective border regions – target misidentification by military air defense operators remains a credible scenario.
Belarus
US operators are to exercise extra caution when operating over, within, in or out of the UMMV/Minsk FIR.
Why? Well, they recently “caused” a commercial aircraft to land and it is not entirely clear how secure the region is and if there are any safety implications for US operators at this time.
Egypt
US operators are to exercise extra caution when operating over, within, in or out of the Sinai Peninsula within the HECC/ Cairo FIR below FL260.
Why? There is ongoing fighting between military and extremist forces and they have anti-aircraft capable weapons.
Iran
US operators are prohibited from operating in the OIIX/Tehran FIR.
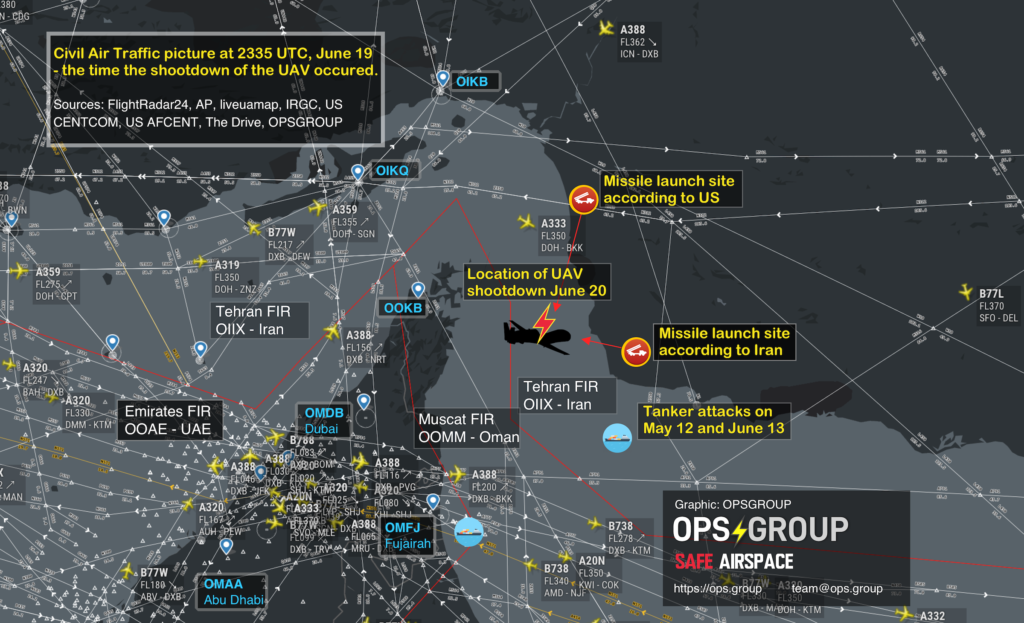
Why? There are signifiant security and safety issues in the region and the US and Iran are not on the best of terms. There was also an aircraft shoot-down due to mis-identification of their anti aircraft defence systems.
Iraq
US operators are prohibited from operating in the ORBB/Baghdad FIR.
Why? Similar to Iran, there are heightened military activities and increased tensions which present and inadvertent risk to US civil aircraft due potential for mis-identification.
Kenya
US operators are to exercise extra caution when operating over, within, in or out of Kenyan airspace east of 40 degrees East longitude (the border region with Somalia), at altitudes below FL260. The caution applies to the ground as well.
Why? Because there’s possible militant activity and with it a threat of damage to aircraft from mortars, rockets and anti-aircraft capable weapons.
North Korea
US operators are prohibited from operating in the ZKKP/Pyongyang FIR, including the oceanic part of the ZKKP/Pyongyang FIR over the Sea of Japan.
Why? Because there are hazards and risk to civil aircraft safety from North Korea due their military capabilities and activities, including unannounced missile and air defense weapons testing.
Libya
US operators are prohibited from overflying the HLLL/Tripoli FIR except for altitudes at or above FL300 “outside of Libyan territorial airspace” – which is basically the international airspace over the southern Mediterranean Sea that is managed by Libya.
Why? Because of ongoing conflict between the government and the Libyan National Army over territory, government control and resources – and all this means fighting, often with weapons which could damage aircraft.
Mali
US operators are to exercise extra caution when operating over, within, in or out of Mali below FL260.
Why? There is a risk of militant and extremist activity and mortars, rocket and anti aircraft fire.
Pakistan
US operators are to exercise extra caution when operating over, within, in or out of Pakistan.
Why? There is a risk of militant and extremist activity and mortars, rocket and anti aircraft fire.
Persian Gulf
Exercise caution operating in overwater airspace above the Persian Gulf and Gulf of Oman in the OKAC/Kuwait, OEJD/Jeddah, OBBB/Bahrain, OOMM/Muscat and OMAE/Emirates FIRs.
Why? There is a lot of military posturing and political tensions in the region and this bit is particularly close to the OIIX/Tehran FIR which is prohibited for US operators.
Somalia
US operators are prohibited operating below FL260 in the airspace of Somalia.
Why? There are active extremists in the region which pose a threat.
Syria
US operators are prohibited from entering the OSTT/Damascus FIR, and should exercise caution if within 200nm of Syrian airspace.
Why? It is a complex and ongoing conflict there, and it poses a risk to US operators.
Ukraine
US operators are prohibited from entering the UKDV/Dneptropetrovsk FIR (the UKFV/Simferepol FIR is ok).
Why? There is ongoing military action and the potential for aircraft misidentification there.
Venezuela
All operations below FL260 are prohibited unless specifically approved or they need to for an emergency.
Why? Mainly poor infrastructure, and political conflict between the two countries.
Yemen
US operators are basically prohibited from overflying the landmass of Yemen, but certain offshore routes within the OYSC/Sanaa FIR are allowed.
Why? Because of ongoing fighting, instability and possible terrorist activity.
An even briefer summary
For further information on the situation in each country and to see the prohibitions and restrictions recommended by other authorities, visit the SafeAirspace site.
The concept of SafeAirspace is this: to have a single source for all risk warnings issued about an individual country, independent of any political or commercial motivation, so that a pilot, flight dispatcher, security department, or anyone responsible for flight safety can quickly and easily see the current risk picture.
Travel Advisories
Travel Advisories and Airspace Warnings are different things. But for US operators flying internationally, it’s worth checking out the latest country-specific Travel Advisories issued by the US Dept of State. Each country’s Travel Advisory also has a link to the local US Embassy website in that country – these will show announcements on all the latest security-related news and incidents there.
Further reading
- US and allied forces have now pulled out of Afghanistan, and the Taliban have taken control of the country. Afghanistan’s airspace is now effectively closed to overflights – the OAKX/Kabul FIR is uncontrolled, and overflying traffic should route around the country. Here is our latest update on what is happening.
- The US reissued their Ukraine warnings in 2021. However, certain regions are Ukrainian airspace are now deemed safe for overflight.
- Information on the aircraft shootdown in Iran, and ongoing concerns with their airspace safety.
- Assessing the risk to routing over or into conflict zones is much more than just an “is there a weapon down there?” question. Gathering and sharing information on airspace risk is still one of the biggest barriers to safety. Are we actively seeking this information, or simply waiting for it to come our way? Read our article.
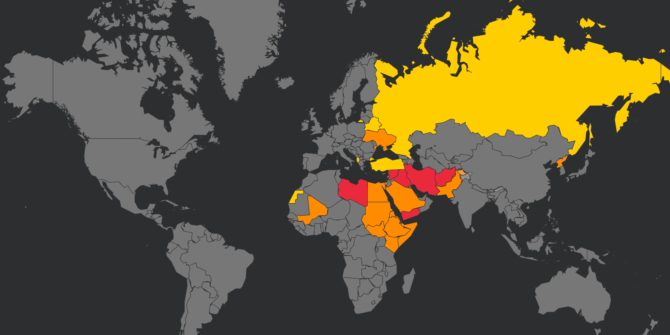
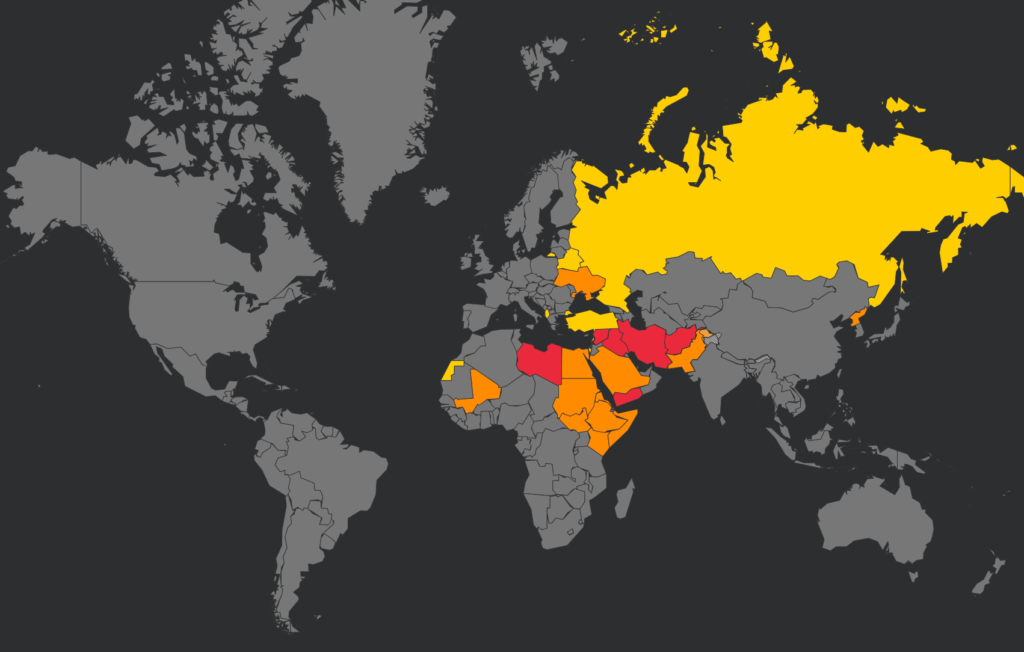

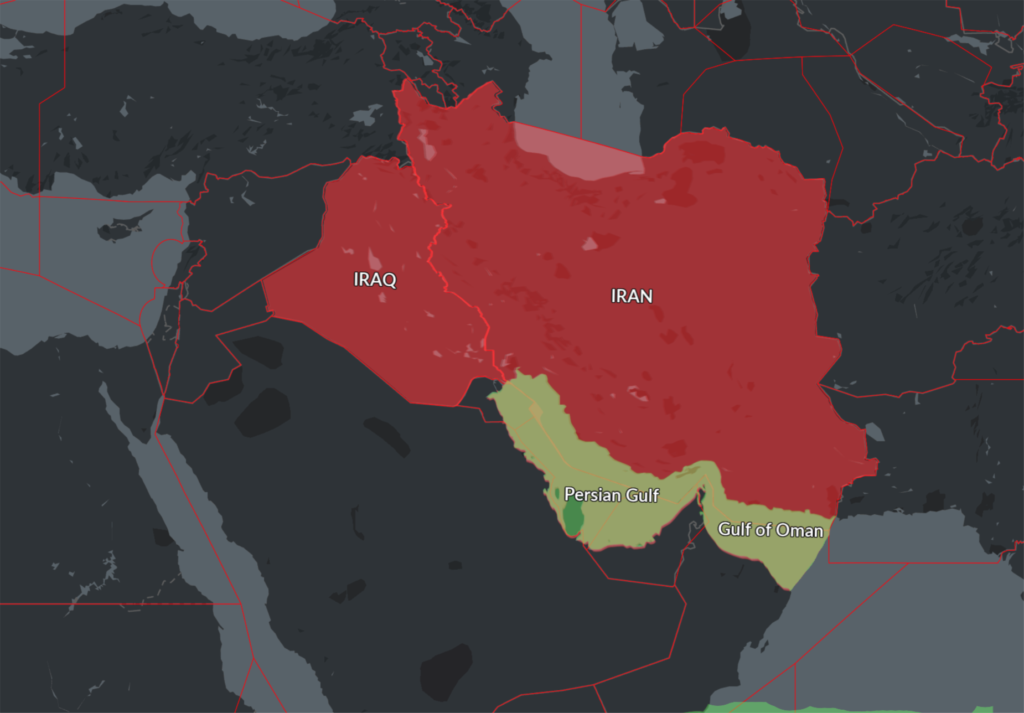 This new Notam represents a further loosening of the total airspace ban on the Persian Gulf and Gulf of Oman initially applied by the FAA shortly after the Iranian missile strike on US military bases in Iraq on Jan 8, which was quickly followed by the shooting down of Ukraine Int Airlines flight 752 in Tehran by the Iranian Armed Forces, having mistaken the aircraft radar return for an inbound missile.
This new Notam represents a further loosening of the total airspace ban on the Persian Gulf and Gulf of Oman initially applied by the FAA shortly after the Iranian missile strike on US military bases in Iraq on Jan 8, which was quickly followed by the shooting down of Ukraine Int Airlines flight 752 in Tehran by the Iranian Armed Forces, having mistaken the aircraft radar return for an inbound missile.