2020 was a heck of a ride. But therein lies the risk – what else might you have missed amongst all the Covid-related noise? Sadly, conflicts and their risks to civil aviation have not taken a break during the pandemic.
As it’s a new year, we thought a summary of Airspace Risk was called for. Here’s what’s making headlines at the moment:
Saudi Arabia & Yemen
Houthi rebels in Yemen are regularly firing explosive drones and rockets across the border into Saudi Arabia, and these usually target airports in the south such as OEAH/Abha and OEGN/Jizan. Their latest attack was on OYAA/Aden airport in late December which resulted in mass casualties.
Saudi Arabia continues to retaliate with airstrikes. The latest was in the capital Sanaa just weeks ago, where multiple munitions landed near the airport.
The risk to aviation is that overflying aircraft may get caught in the crossfire or might be misidentified by Saudi air defences. Active terrorist groups in Yemen may also use anti-aircraft weaponry to target foreign interests.
The FAA prohibit all US operators from entering most of the OYSC/Sanaa FIR at any level. Only two airways are allowed, and they are well off the coast – UT702 and M999.
There are no restrictions on Saudi Arabia but use caution in the southern regions. France and Germany have issued their own warnings.
SafeAirspace Yemen page – click here.
SafeAirspace Saudi Arabia page – click here.
Iraq
Rocket attacks on military interests at airports have become a common occurrence. They are generally fired by local militia without warning. ORBI/Baghdad is frequently targeted, along with other airports including ORER/Erbil. There is a clear risk to aircraft at low levels.
US relations were further strained through 2020 with multiple attacks on the US embassy in Baghdad. The tensions escalated to a point where the US considering closing it.
Foreign aircraft continue to be at risk from armed militia who have access to portable anti-aircraft weaponry, while misidentification by the air defence systems of multiple foreign forces in the country is also possible.
The FAA has extended its ban on US operators entering the Baghdad FIR at any level. Even though the SFAR says you can enter above FL320, the long-running Notam KICZ A0036/30 says otherwise.
SafeAirspace Iraq page – click here.
Syria
There have been several recent Israeli airstrikes on targets throughout Syria. In late December there are reports that Israeli fighters transited Lebanese airspace at low level causing alarm in Beirut before attacking targets in Western Syria. Just weeks ago, several sites around Damascus were targeted by Israeli missiles.
The primary risk is that aircraft may be misidentified by Syrian air defence systems which are regularly activated. Civil operators may get caught in the crossfire as missiles may erroneously lock on to the wrong aircraft.
The FAA are taking no chances – the ban on US operators entering the OSTT/Damascus FIR at any level has been extended a full three years to 2023.
SafeAirspace Syria page – click here.
South Sudan
Just this week ICAO issued a concerning warning about the risk to aircraft operating below FL245 in the HSSX/Khartoum FIR over South Sudan, or flying in and out of HSSJ/Juba. They are ‘gravely’ concerned about ATC disruptions, a lack of contingencies, inadequate training of controllers, limited info about equipment outages and a lack of co-ordination with other ATS units.
SafeAirspace South Sudan page – click here.
Emerging Conflict Zones
2020 saw three new conflict zones emerge, here is what is happening with them now.
A civil conflict erupted in October last year in the Tigray region of Northern Ethiopia. The government went to war with the TPLF – a regional force seeking independence.
The region’s airports were closed and TPLF showed an intent to internationalise the conflict by attacking aviation interests. They fired rockets into Eritrea targeting HHAS/Asmara, and also attacked multiple airports to the South of the Tigray region.
Two airways were closed (T124, and M308) with no explanation of the risk. Other airways remained open but uncomfortably close to the fight – especially UG300, UN321 and UL432. No airspace warnings were issued despite the dangers.
What’s the latest?
In late November Ethiopian forces captured the region’s capital Mekelle and regained control. Remaining TPLF forces have retreated leaving behind a humanitarian disaster and a vow to continue the fight. Since then, the airway closures have been removed and things have gone quiet, but an airspace risk remains – armed militia continue to be active in Northern regions and may be looking to make a statement. Be wary of operating in the area.
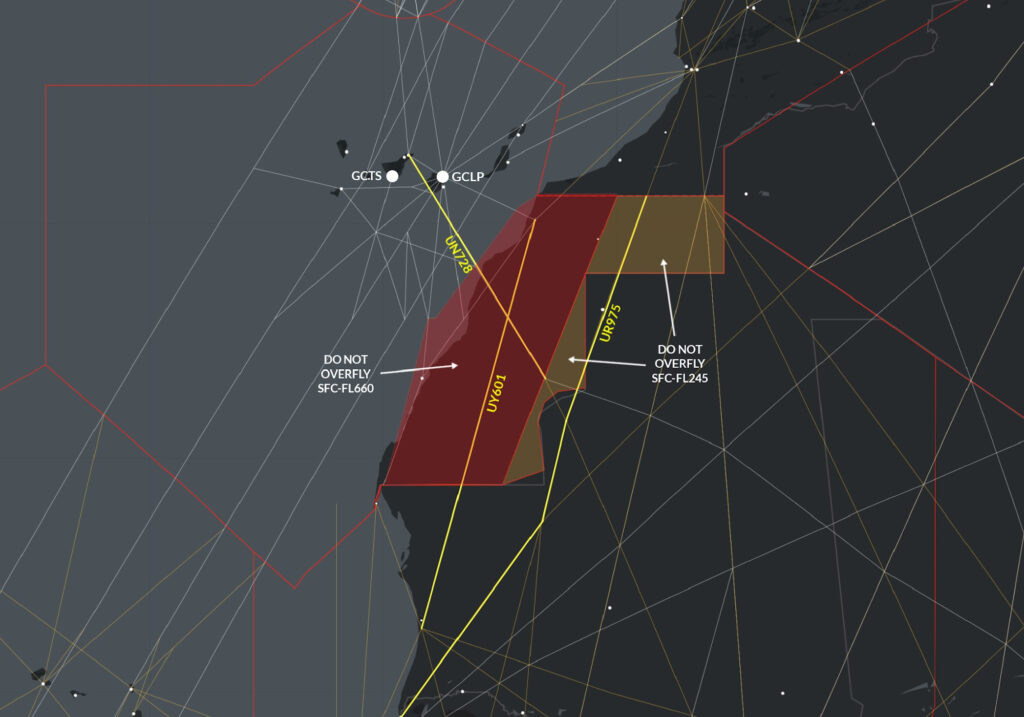
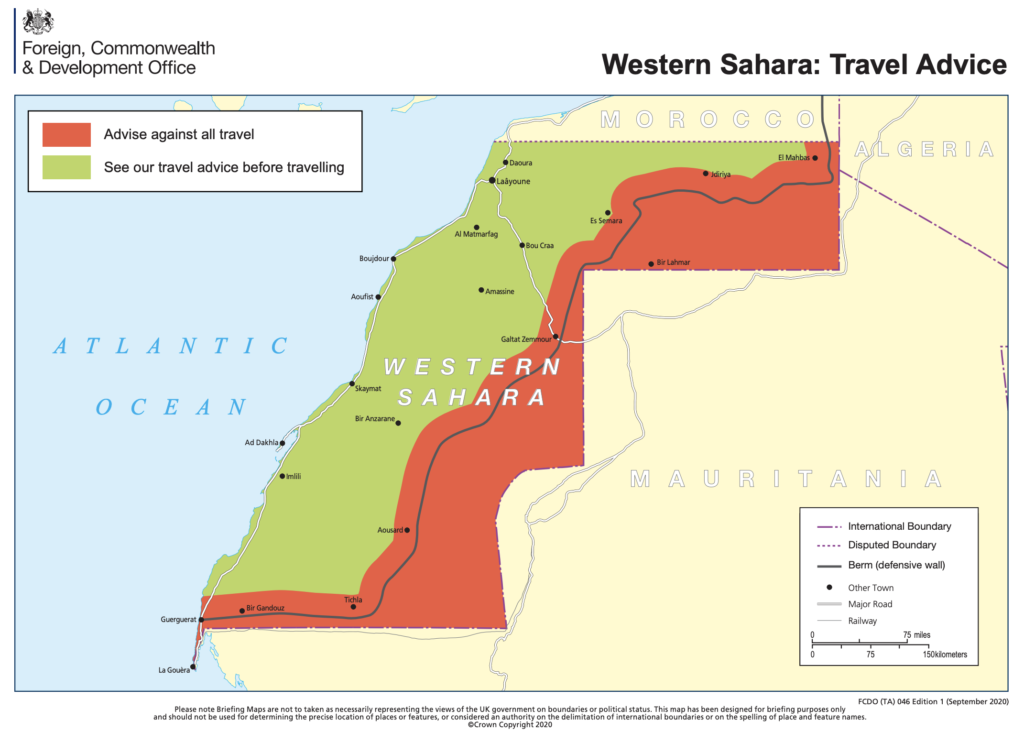
Late last year the region’s independence movement (the Polisario) declared war on Morocco for breaching a ceasefire agreement. The FAA published a warning that the Polisario might have access to anti-aircraft weaponry left over from previous conflicts.
What’s the latest?
It is still an active conflict zone. The fight has reached the international stage after the US declared their support for Morocco. The Polisario have indicated they are willing to at least talk, but so far have not put down their weapons. So, it is a wait-and-see type deal.
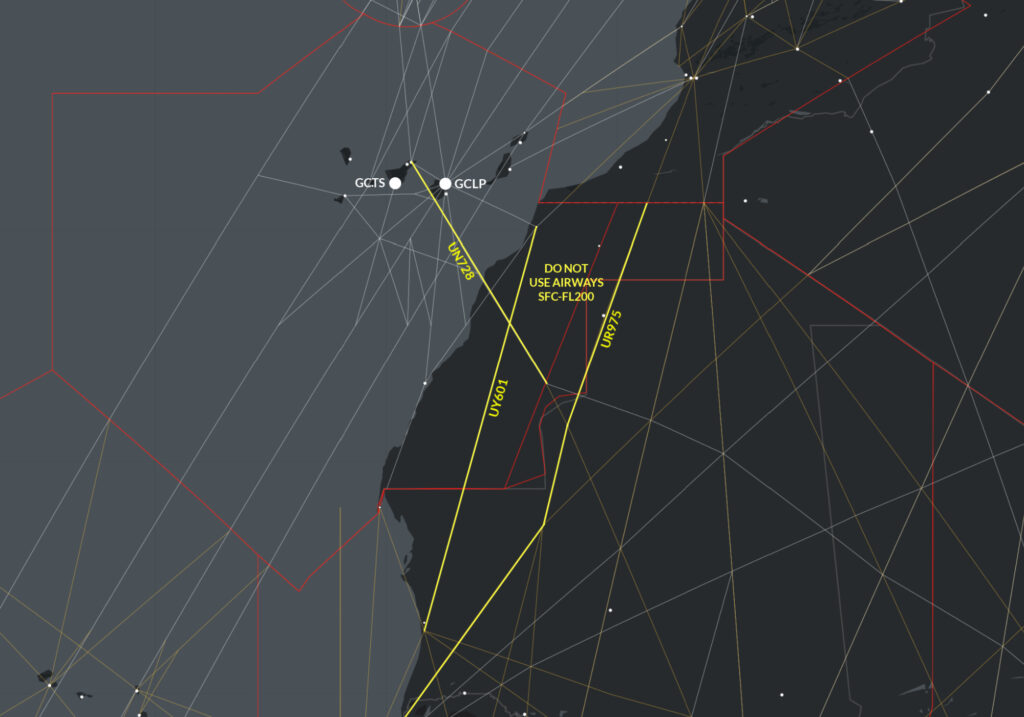
The risk to overflying aircraft remains. The GCCC/Canarias FIR keep extending a Notam advising operators to not fly below FL200 on the following airways: UY601, UN728 and UT975. However, the reason is still missing: because of the risk of anti-aircraft fire. The GOOO/Dakar FIR haven’t issued any warnings despite the threat. Take care if operating in the area.
In September last year, an ethnic conflict erupted over a disputed territory in Western Azerbaijan – Nagorno-Karabakh. The fight was between Azerbaijan and Armenia.
As a major air corridor for en-route traffic, there were significant flight disruptions. Azerbaijan swiftly closed all but one west/eastbound airway and routed traffic via Georgia. Armenia asked aircraft to take extra fuel and expect re-routes. The conflict was short but intense, with heavy artillery fire from both sides. The conflict eventually spread beyond the contested regions with longer range weapons. The entire border region posed a risk for civil aircraft.
What’s the latest?
For once the news is good. In November a ceasefire agreement was signed with the help of Russia. Armenia effectively lost and withdrew from the region and the conflict was officially over. Armenia removed its airspace warning, while Azerbaijan re-opened the affected airways and a large section of airspace near the border.
With the conflict now over, and no new reports of significant fighting since the peace agreement in November, direct crossing traffic between the two countries is now technically possible again. However, most East-West flights are currently still electing to go further north instead, connecting between Azerbaijan and Georgia’s airspace, avoiding Armenia.
What about Safeairspace.net?
Our conflict zone and risk database is updated constantly. We assess risk with official sources and build a simple picture for you of those need-to know-places.
There are currently 5 regions which are assessed as a Level 1 Risk – No Fly. These are: Iraq, Iran, Yemen, Libya, and Syria.
Head over to SafeAirspace.net and take a look. With a single click you can download a risk briefing of the entire world in just a few pages of nice simple English.
The mission of SafeAirspace is this: to provide a single, independent, and eternally free resource for all airspace risk warnings, so that airlines and aircraft operators can easily see the current risk picture for unfamiliar airspace. If you know of a risk not listed on the site, or you have anything else to add, please get in touch with us at news@ops.group