In Short: Worldwide the SAM threat is deemed to be “low” by ICAO with the caveat that this can change quickly when flying over or near conflict zones. The best risk mitigation is centred around which airspace you are operating over and what information you have access to. As we have explained before: There is no safe altitude from a large SAM.
 What are surface-to-air missiles, and who has them?
What are surface-to-air missiles, and who has them?
Surface-to-air missiles (SAMs) are large, complex units, with the capability of reaching aircraft at cruising levels well above 25,000 ft, and they are designed to be operated by trained military personnel.
They are distinct from Man Portable Air Defence Systems (MANPADS), which are the smaller, shoulder-launched systems, the most dangerous of which being the FIM-92 Stinger which has an operational ceiling of 26,000 ft.
SAM systems vary but they are all designed to track and destroy military targets in flight. Due to the size and predictable flight paths, civil aircraft represent easy and highly vulnerable targets.
Many SAMs are mobile and can be moved quickly between locations. Many are located on warships. It is estimated that more than 70 States around the world have acquired SAMs as part of their military capability. A small number of non-State actors (i.e. militant groups) have also reportedly acquired SAMs, but as they require a radar system as part of the mechanism, they may not have the technical capability to use them. To date, SAMs have never been used by terrorists.
What has happened in the past?
There have been three documented occurrences where aircraft destruction has occurred due to SAM attacks.
The risk of intentional attack
To date, no documented case of intentional SAM attack on a civilian aircraft has been identified. In the case of MH17 and Iran Air, both occurred during periods of military conflict or high tension, whilst Siberia flight 1812 was shot down during a military training exercise.
ICAO say that “with regard to the States and non-State actors that currently do have access to SAMs, there is no reason to believe that the intent currently exists to target civil aviation deliberately.” And with regards to terrorist groups (as opposed to militarized forces), they say that “even where intent may exist there is currently no evidence of capability (in terms of hardware and trained personnel).”
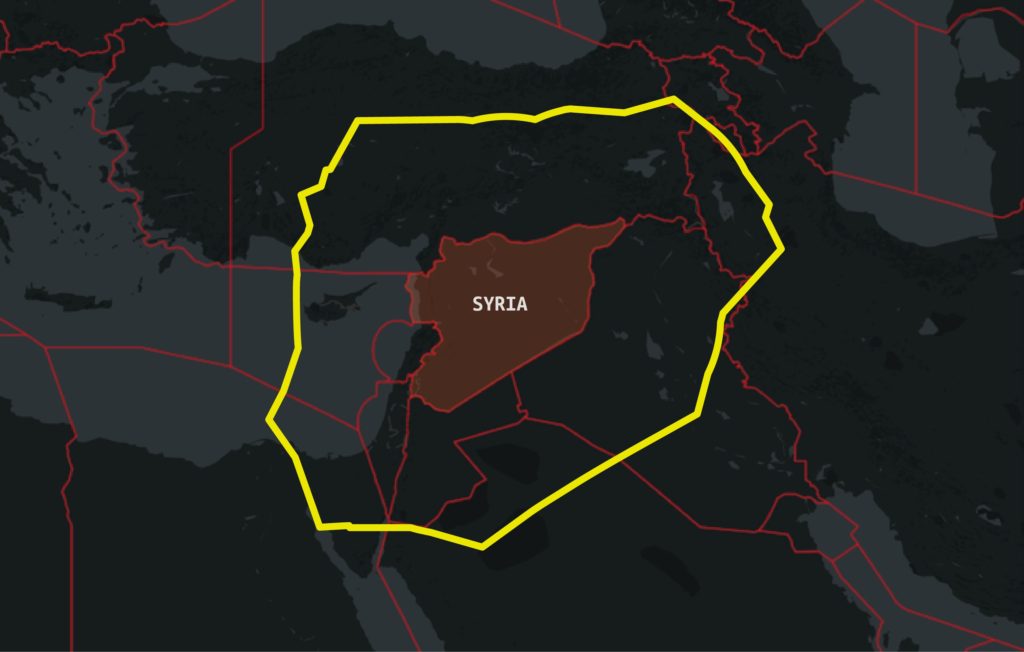
Overall, the current risk to aviation from intentional SAM attack is therefore currently assessed to be low, the key caveat being to avoid overflying airspace over territory where terrorist groups tend to operate – normally areas of conflict where there is a breakdown of State control.
The risk of unintentional attack
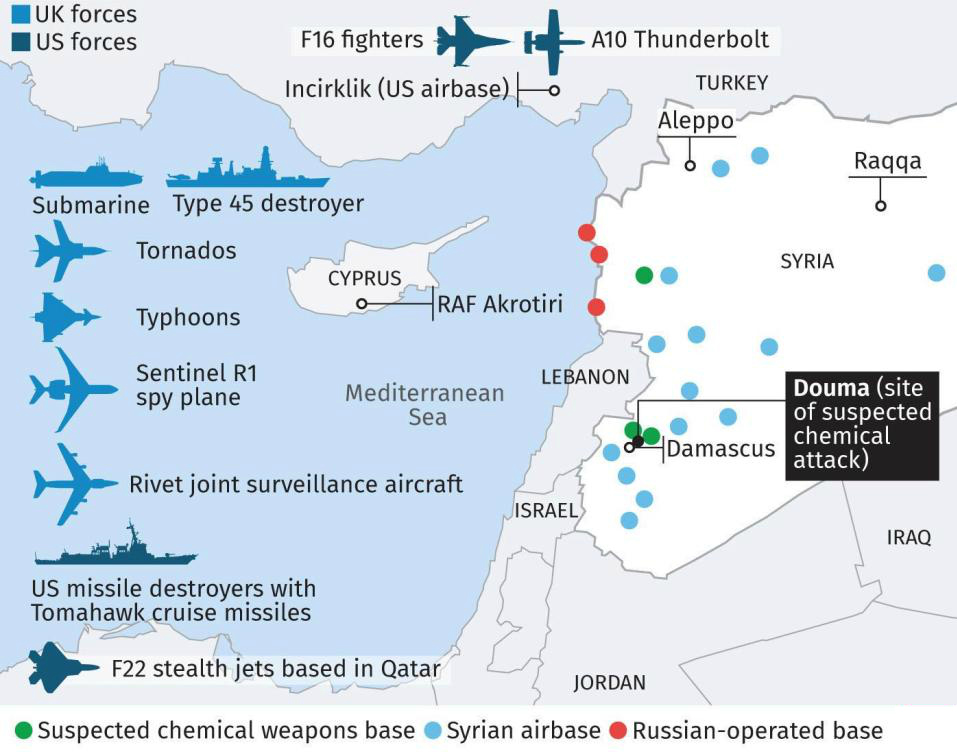
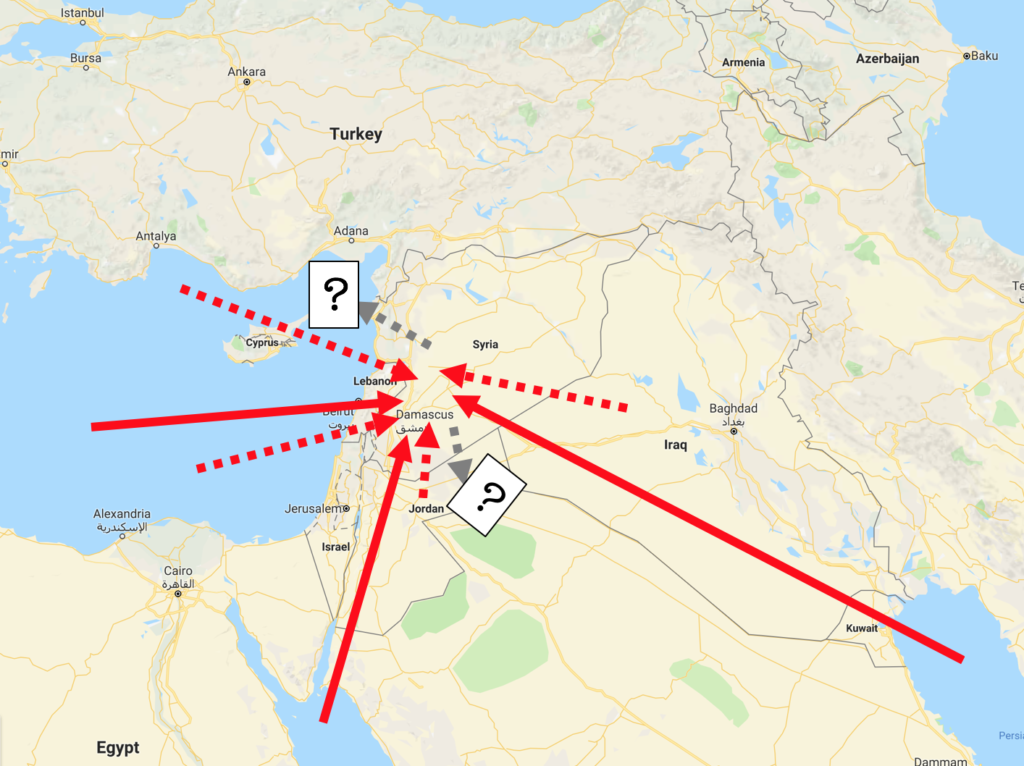
Past events show us that the higher risk to civil aviation is from unintended and unintentional attacks when flying over or near conflict zones – missiles fired at military aircraft which miss their target, missiles fired at civil aircraft which have been misidentified as military aircraft, and missiles fired by State defence systems intended to shoot down other missiles.
Areas where there are armed conflicts going on clearly present an increased risk of an unintentional attack. But when assessing the risk of overflying a particular conflict zone, here are some more specific questions to consider:
Are there increased levels of military aircraft flying around in the region?
This could be anything from fighter jets being operated in a combat role, or for hostile reconnaissance; remotely piloted aircraft; or military aircraft used to transport troops or equipment. If military aircraft are one of the most likely targets for intentional attacks, then the chances of civil aircraft being mistakenly targeted increases in those areas where there are lots of military aircraft zipping around.
Are there likely to be a bunch of poorly trained or inexperienced personnel operating SAMs in the region?
This may be difficult to evaluate, but the risk is likely to be highest where SAMs may have been acquired by non-State actors. The risk is also likely to be higher in places where there is less of a robust command and control procedure for launching missiles, thus increasing the risk of misidentification of civil aircraft.
Is the territory below the airspace fully controlled by the State?
If not, and there are some areas controlled by militant or terrorist groups, the information on the presence and type of weaponry in such areas, as well as the information on who controls them, may not be readily available. In such regions, the information promulgated by the State about the risks to airspace safety may therefore not be 100% reliable.
Does the route pass over or near anywhere of particular importance in the context of the conflict?
These could be areas or locations that may be of strategic importance or sensitivity in the conflict, such as key infrastructure or military sites, which might be considered potential targets for air attack and would therefore be more likely to be guarded by SAMs.
Ultimately, risk mitigation is centred around which airspace you are operating over and what information you have access to. But as has been reported in the past, history has shown us that badly-written information published by the State often does little to highlight the real dangers posed by overflying conflict zones.
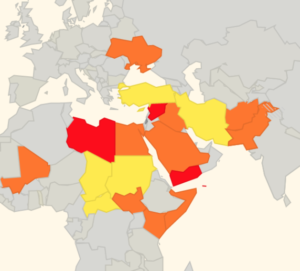 There is some evidence to suggest that more States are starting to provide better guidance and information to assist operators in making appropriate routing decisions, but we think this still has some way to go.
There is some evidence to suggest that more States are starting to provide better guidance and information to assist operators in making appropriate routing decisions, but we think this still has some way to go.
That is why we have been running our safe airspace map to provide guidance to assist operators in determining whether to avoid specific airspaces around the world.
Extra Reading: