The annual posturing between the DPRK (North Korea), and the US/South Korea, follows a fairly regular pattern each year. The cycle involves escalating threats (by both sides), a cooling off process, a long period of nothing, and then a resumption of threats. History tells us that there is nothing to fear, because this is always the way it works on this peninsula, but then a slightly less micro view also tells us that we don’t always make the correct risk assessment.
Prior to MH17 (B777 shootdown, Ukraine), our view of missiles in the commercial aviation community was a little casual. Post-incident, the rule of ‘overflights are safe’ as a standing principle was removed, and suddenly a whole lot more interest was applied to what was going on underneath the airways, even if we were up at FL350.
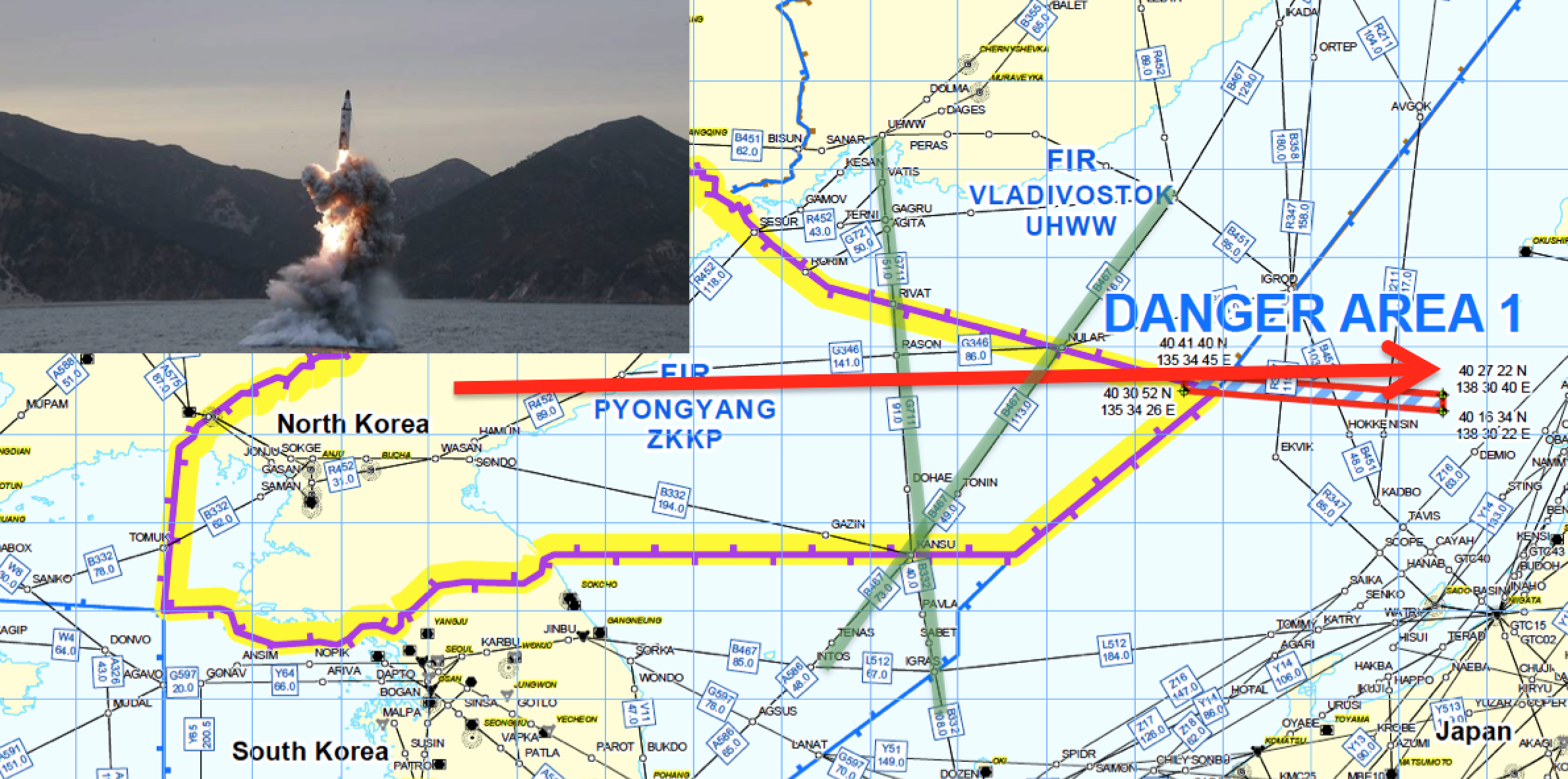
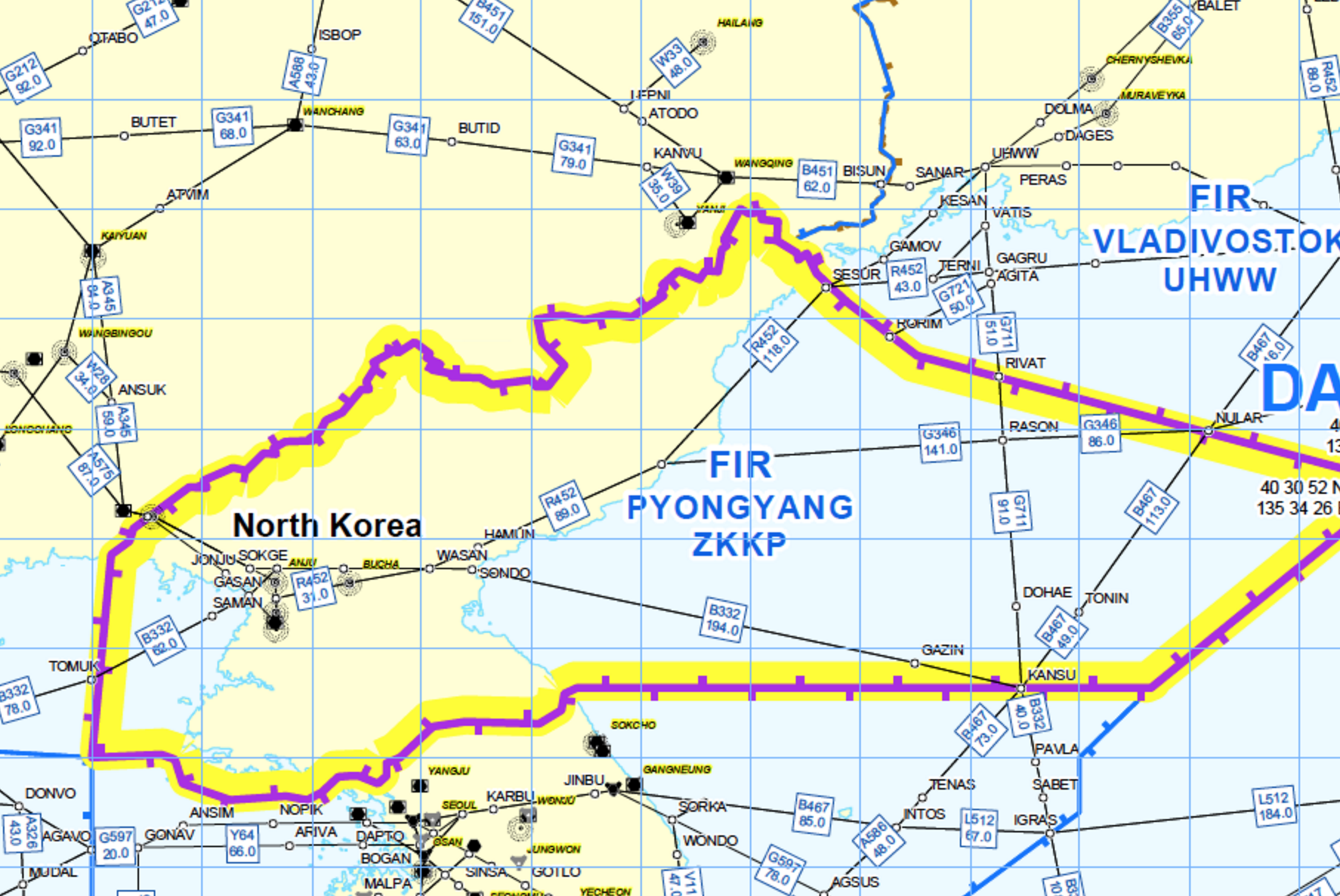
In specific terms, over the last fortnight, North Korea has been launching short and medium range missiles like they are going out of style. Nobody in Pyongyang has any intention of aiming them at civil airliners, but the objective is not where the risk lies. Late last year when Russia fired 30+ missiles into Syria, at least 5 of them went off course (including way above where they should have flown).
This wayward tracking is the greater part of our concern, for all flights within the Pyongyang FIR (ZKKP). Most international overflights are using the North-South airways over water to the east of the landmass, and it’s worth considering that the missiles launched in the last week have been directed out over the sea in this direction (not coincidentally in the direction of Japan, who isn’t on the DPRK Christmas card list either).
US Operators are in any case restricted by SFAR79, but everyone else should be keeping a close eye on their North Korean overflight plans. (If this hasn’t put you off, you can read the full North Korea overflight permit requirements).