You might have seen the headlines a week or so ago. On January 23, Saudi Arabia’s capital Riyadh was attacked by a ‘hostile air target’ – likely an explosive ‘kamikaze’ drone. Saudi air defences destroyed it, causing a loud explosion over the city and flight disruptions at OERK/Riyadh.
Then a few days later it happened again. Another big bang in the skies of Riyadh and more flight disruptions. Plenty of people caught it on camera. But the silence from official channels was deafening.
So what? Isn’t there is always stuff in the news about drones over there?
Yes. They’re sporadically sent over the border from Yemen by the Houthi – the folk who overthrew the Yemeni government back in 2014. Southern regions are usually the worst hit and occasionally Jeddah and Riyadh are targeted just to remind Saudi Arabia that they can.
But here’s the kicker: this time it probably wasn’t them.
How Do You Know?
Firstly, the Houthi have adamantly denied they were to blame. They’ve actually gone out of their way to distance themselves from the attack. So why should we believe them? Because of the status quo – they want to make headlines. Their attacks on Saudi Arabia are a demonstration of their firepower and willingness to target anywhere in the country. They’re even known to claim responsibility for attacks that weren’t theirs.
Secondly, someone else has already put their hand up for the attack – a group of militants in Iraq called the Alwiya Waad al Haq. The Who? The ‘Brigades of the Righteous Promise’. It’s a fancy name but the takeaway is this: someone new is apparently taking shots at Saudi Arabia from Iraq.
Here’s why
Saudi Arabia and Iran don’t get along. The reasons are long and complicated and you can read more about them here. But in a nutshell, religious differences and a desire for regional dominance are the cause of the ongoing conflict. The attacks on Riyadh are a worry because they may reflect a changing way that Iran asserts its dominance throughout the Persian Gulf – by proxy.
Proxy conflicts are a thing. It means when someone is doing the hands-on fighting for somebody else. Remember those Brigades of the Righteous Promise people? It is alleged that Iran may have put have put them up to it, and supplied the firepower to do it.
There’s no shortage of independent militia in Iraq. They’re difficult to trace and new ones emerge seemingly from nowhere – so much so that they’re sometimes known as ‘shadow militia.’ In reality, they are usually a cover for larger and much more well-known groups. In this case, possibly the Hezbollah – one of Iran’s largest proxies. By hiding behind different names they can cause confusion, unpredictability and can divert blame away from the prime suspects.
It is possible that Iran may now start using these proxies more often for attacks on its regional adversaries.
So why is this an aviation issue?
We get twitchy when anyone is firing things into the sky. This way of fighting is unpredictable and the weapons being used are getting more sophisticated and can cover large distances.
Case in point. Back to the Brigade guys – since their alleged attack on Riyadh they have since threatened to attack the Burj Khalifa in Dubai, and also Abu Dhabi airport. Whether or not their threats can be taken seriously remains to be seen – but if the attack on Riyadh is anything to go by, they might have the weapons and intent to do it.
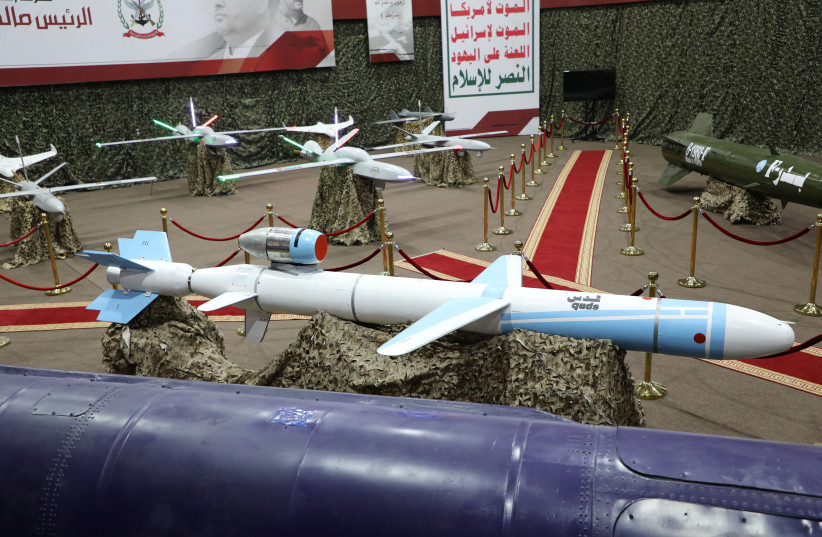

A drone similar to the ones believed to have targeted Riyadh.
For aircraft, there are a few threats to be aware of:
- Misidentification by sophisticated air defence systems.
- Being caught in the cross fire.
- Simply being in the wrong place at the wrong time. Airports are often a prime target.
What can we do about it?
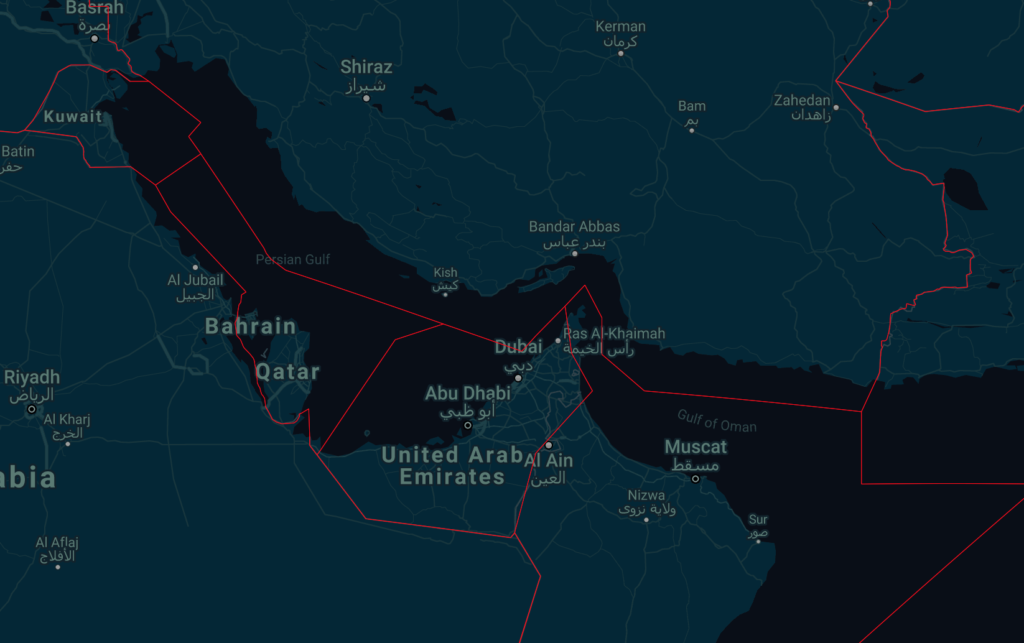
Continue to monitor Safeairspace.net for airspace warnings – it is our database of airspace risk and we update it all the time. Head over there and take a look – there are multiple warnings for the Persian Gulf region including four ‘no fly’ countries: Syria, Iraq, Iran and Yemen.
Understand ESCAT rules. Or you might know them as SCATANA. Either way they are a protocol for getting you out of dangerous airspace and fast. ATC may divert you clear of an FIR or ask you to land. They’re in use in Southern Saudi Arabia – but can be applied at short notice to any airspace where the risk is high. ESCAT procedures are published in GEN 1.6 of Saudi Arabia’s AIP. If you don’t have a login, you can see the relevant section here.
Lastly, carry out your own risk assessment and know what’s going on down there. Just because airspace is open doesn’t mean that it’s safe.


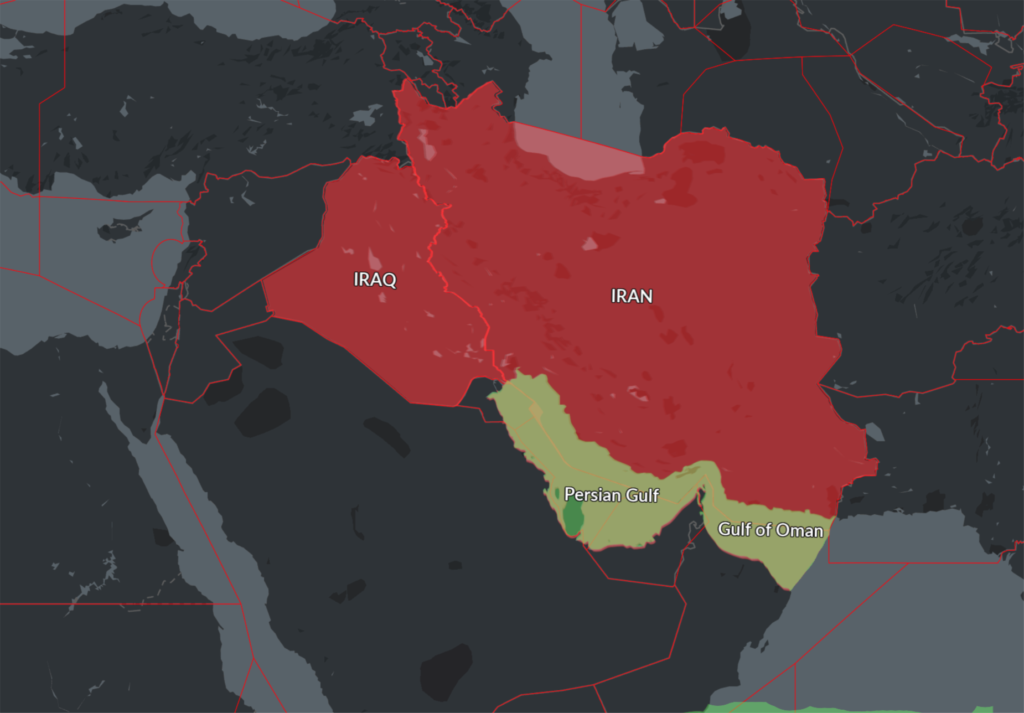 This new Notam represents a further loosening of the total airspace ban on the Persian Gulf and Gulf of Oman initially applied by the FAA shortly after the Iranian missile strike on US military bases in Iraq on Jan 8, which was quickly followed by the shooting down of Ukraine Int Airlines flight 752 in Tehran by the Iranian Armed Forces, having mistaken the aircraft radar return for an inbound missile.
This new Notam represents a further loosening of the total airspace ban on the Persian Gulf and Gulf of Oman initially applied by the FAA shortly after the Iranian missile strike on US military bases in Iraq on Jan 8, which was quickly followed by the shooting down of Ukraine Int Airlines flight 752 in Tehran by the Iranian Armed Forces, having mistaken the aircraft radar return for an inbound missile.