If you have not heard of the IFP Information Gateway then here is a little summary for you. It is the Instrument Flight Procedures Information Gateway which is, according to the FAA who run it, your centralized instrument flight procedure data portal.
It’s a handy site because it provides you with a single-source, one-stop-shop, first place to visit if you need info on any of the following:
- Charts
- The IFP Procedures plan
- IFP Coordination (forms and things)
- IFP Documents
- IFP Request form – this is where you can submit a request or query on an IFP. SO if you fly somewhere and think an IFP needs creating, amending or cancelling, you can do it here!
And this isn’t just for US pilots – it is pretty handy for anyone flying into the US who flies IFR procedures.
The Optimisation Project
This is a major project that the FAA are undertaking. They are reviewing their entire inventory of equipment and procedures as part of a plan to modernize the National Airspace infrastructure – to improve airspace and airport efficiency and safety.
The NAS covers an area of something like 30 million square miles, so it is a big project.
What is the plan?
The introduction of PBN (performance based navigation) is a big part of the modernization. If you fly into the US then you need to know about this, because it is going to mean changes to routes and procedures, airspace and equipment required.
Charts are being updated to remove unnecessary clutter. In 2020 they cancelled 1,000 procedures and took out things like circling minima on charts that no longer needed it. You need to know about this because it will impact chart validity, and things like minimus are airports you might use.
As for the inventory check – they are reviewing all the procedures at airports and deciding which to keep, which to cease, and which just plain old need updating. This will start with the decommissioning of any ancient VORs and NDBs which no longer support the operations network. You need to know about this because there will be ongoing changes to the approaches available at airport.

Who knows how to follow that yellow arrow?
Give us some more details on the inventory checks
The FAA are going to review all procedures.
Why?
Well, because having looked over some data they reckon at least 20% of current IFPs have pretty limited benefits to the NAS. If procedures are not being used then retiring them means lower admin, maintenance and training costs. It also means more efficient and effective airspace management, which means improved safety and access.
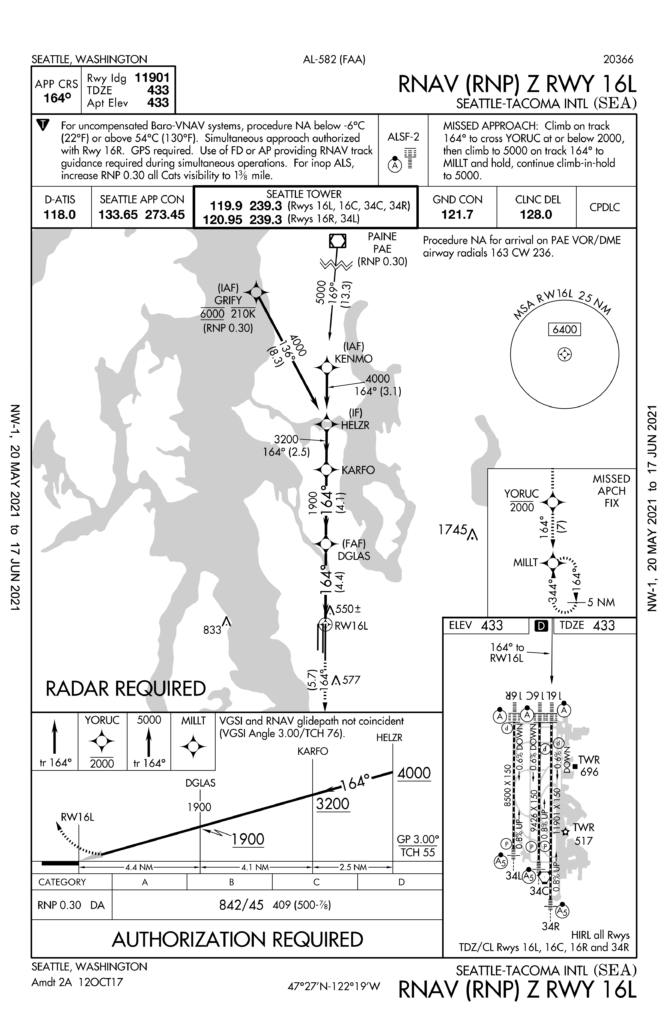
Take KSEA/Seattle for example. They have an RNAV RNP approach and a GPS approach for runway 16L. The RNAV RNP was only flown 17 out of a whopping 191,448 IFR arrivals.
It has higher minimum and an identical flight path to the GPS approach so there is really no reason for this approach to exist.
KPAE/Paine Field is another one worth looking at. It has a VOR-A approach which was only flown 95 times out of 10,348 IFR arrivals. It is under-utilized, costs a bunch to maintain and there are plenty other options. So it is a good one to chop.
What about KSBA/Santa Barbara airport and their VOR or GPS approach runway 25? This was also significantly under-utilized, being flown just 1,732 out of 17,174 arrivals. However, it is the most commonly used approach for GA traffic, and is the only one available when the wind is favoring that runway. Not such a good one to delete.
The IFP plan won’t just review data and statistics, it also engages with the folk using the IFPs to make sure changes are benefiting those it needs to benefit. Santa Barbara won’t lose the procedure just yet, although they might get itself a nice new space-based one out of this at some point.
Comments and feedback
If you fly into airports and have comments or feedback on IFPs then get in touch, either by filing in the form, or emailing at 9-AMC-Aerochart@faa.gov. This project is a long, ongoing one, but one that will benefit any operator who flies in or out of the US, and there are opportunities there to provide input.
Check out the info
- You can watch the full Stakeholder Presentation here if you want some more info on it.
- You can visit the official FAA IFP site here.