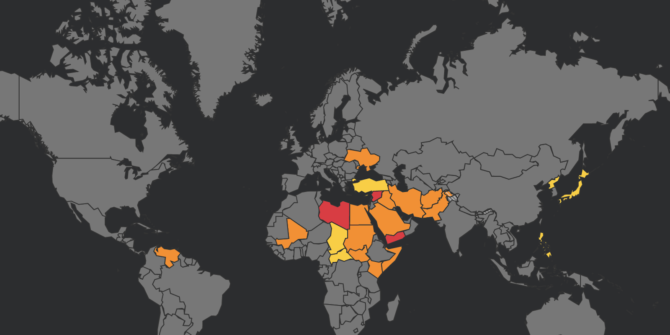
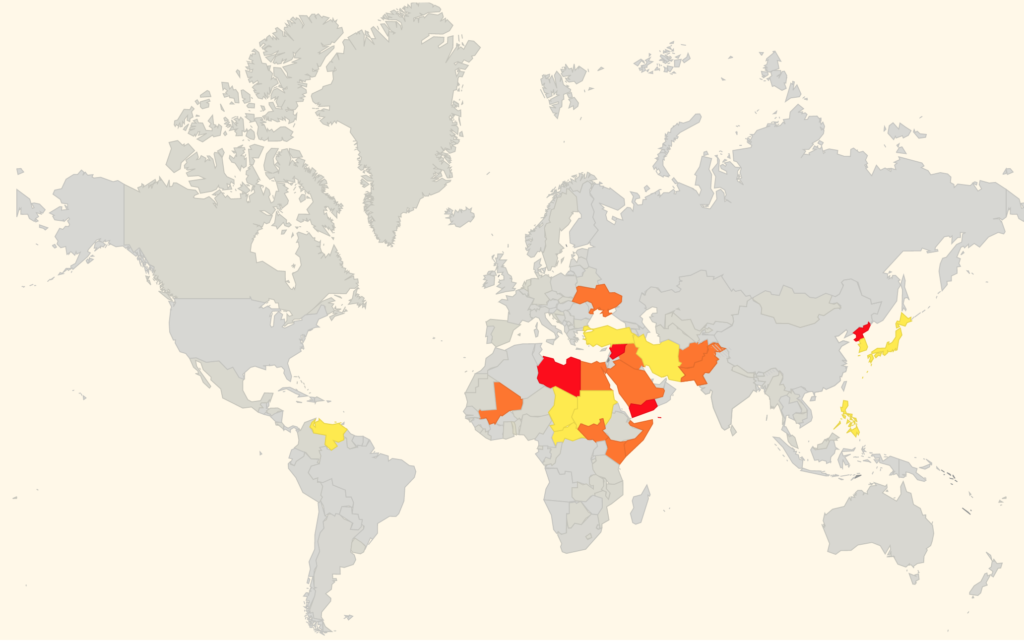
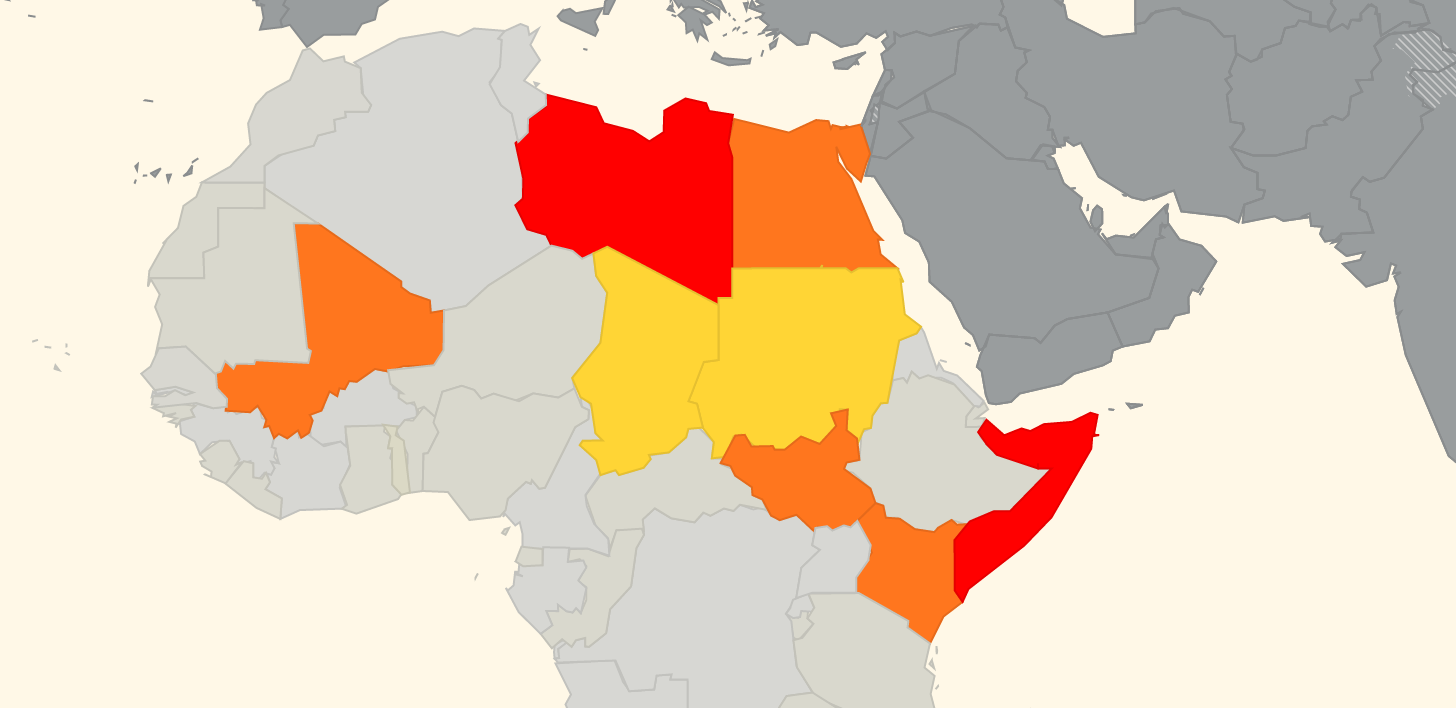
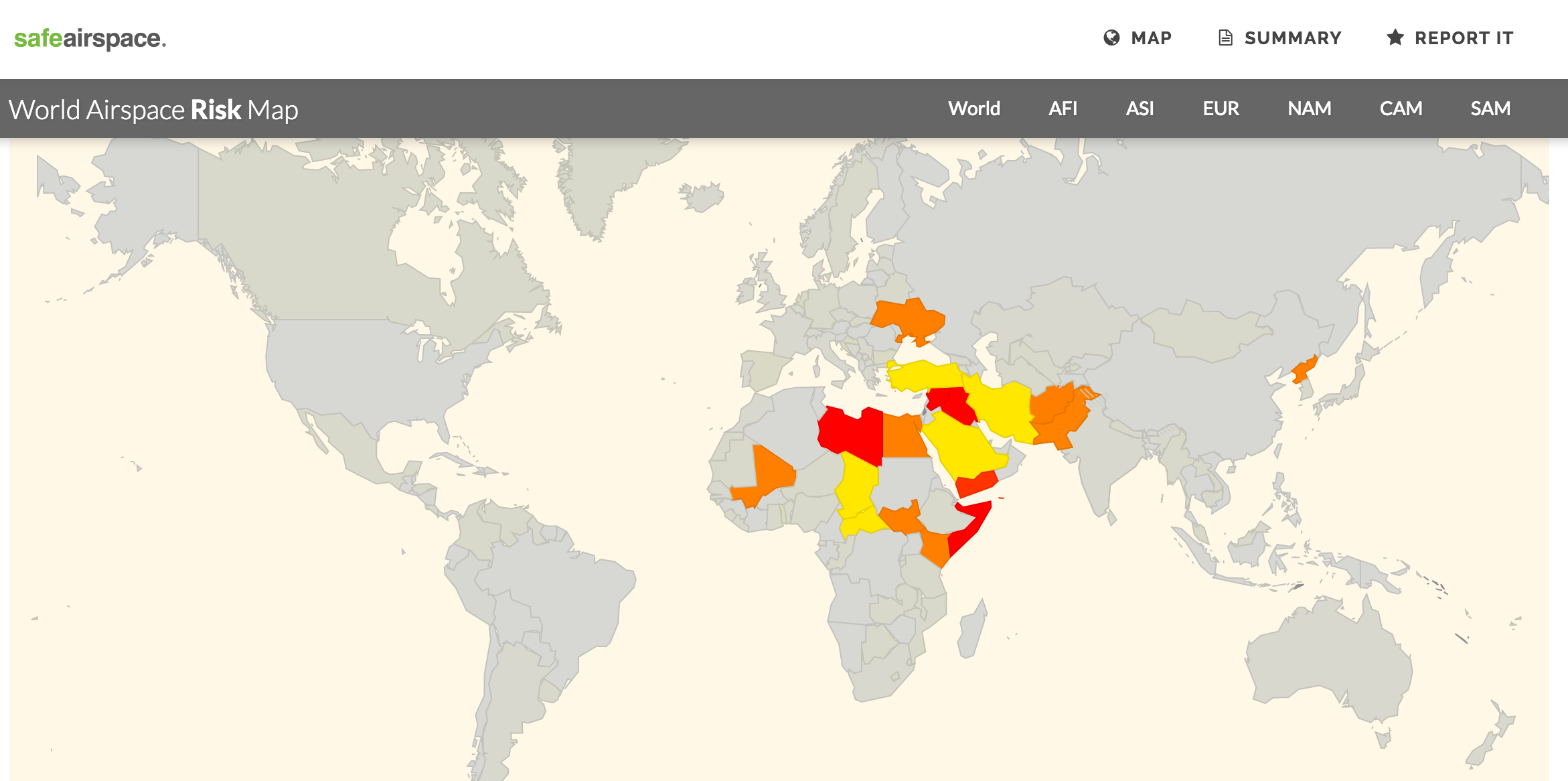
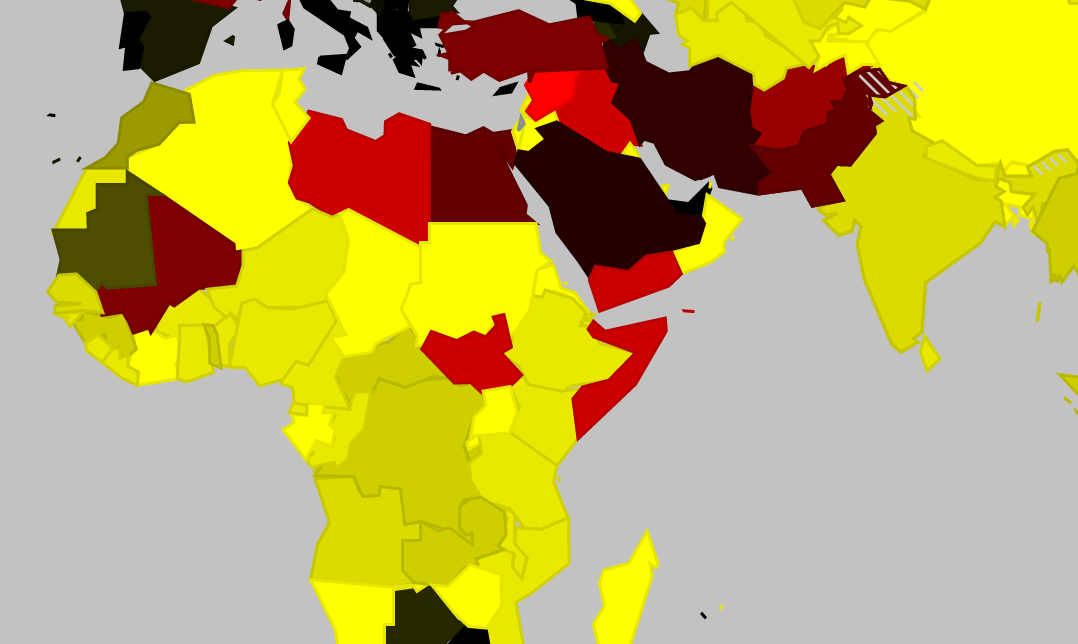
To make it even easier to get a current risk picture for International Flight Ops, we’ve added a bunch of new features to the Conflict Zone & Risk Database at SafeAirspace.net.
Thank you to all OPSGROUP members – all our airlines, aircraft operators, pilots, dispatchers, and industry colleagues who’ve made this possible. Now we have a simple, single source of information for all risk warnings, analysis, that includes our Risk Radar project (so for the first time we can see what other operators are doing), all state warnings, and the ability to auto-generate a live Summary PDF of the current situation.
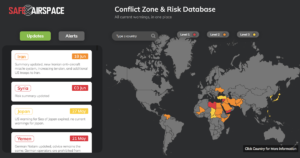
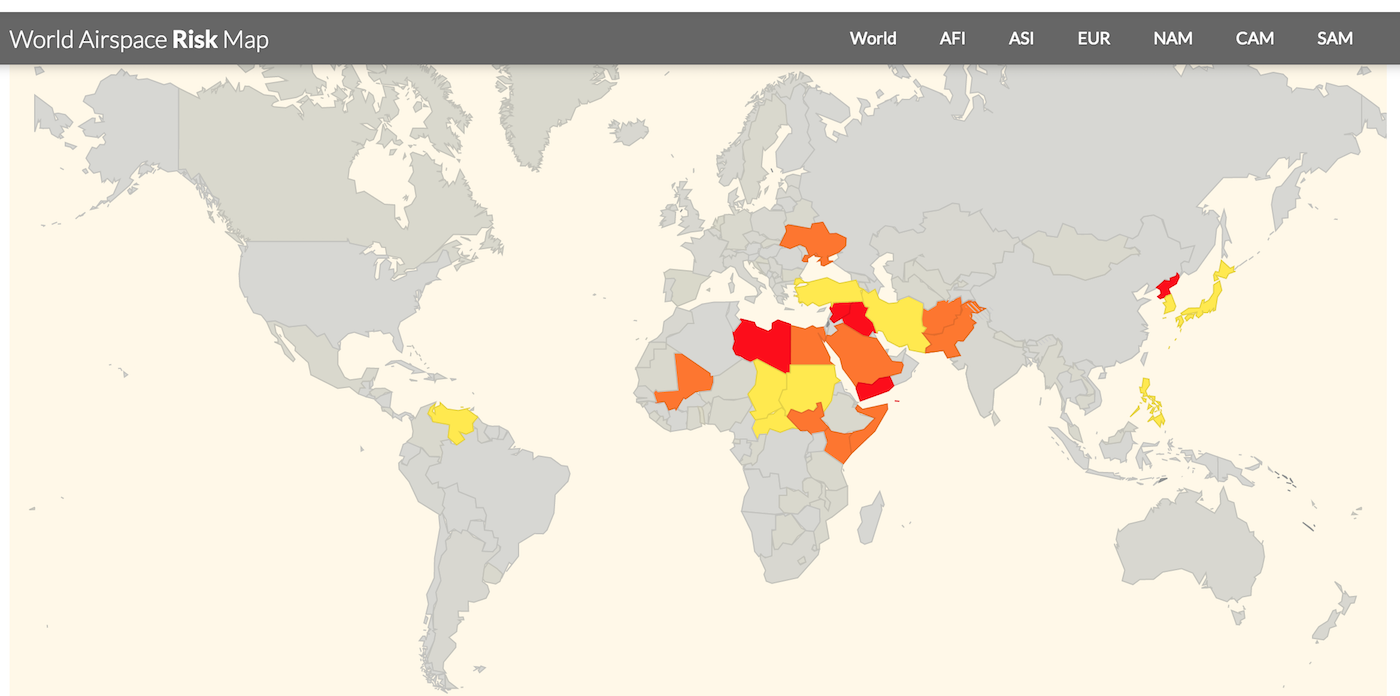
Start at SafeAirspace.net, where you have the current risk map, and feed of Updates and Alerts:
On each country page, you will now see Risk Radar information like this:
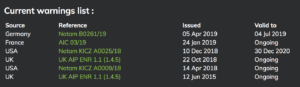
For each country, you’ll see the current list of warnings, both from the country concerned and other states:
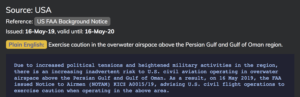
Scrolling down, you’ll get the current Notam/AIC/AIP reference and a copy of the text:
For each country, there is a Summary and Analysis, so you get some background on why these warnings exist:
A new feature is the ability to generate a live summary into a PDF, so you can print out everything into one document to share with your crew, dispatchers, and security team:
You can download an example of the PDF, generated on June 19th, 2019, here:
PDF Summary – World Airspace Risk at SafeAirspace.net

Download PDF, 800kb
You can generate your own live PDF here.
About the Conflict Zone & Risk Database
The Conflict Zone & Risk Database provides a single, independent, and eternally free resource for all airspace risk warnings, so that airlines and aircraft operators can easily see the current risk picture for unfamiliar airspace.
Safe Airspace is an initiative from OPSGROUP, an independent organisation with 5000 members, made up of airlines, corporate flight departments, private operators, charter operators, military, and government.
The Conflict Zone & Risk Database was launched in September 2016 as the lifespan of the ICAO CZIR was coming to a close, keeping the work ICAO did on the project alive, and providing the autonomous platform needed to make the concept work.
Objective – one single source
A single source for all risk warnings issued about an individual country, independent of any political or commercial motivation, so that a pilot, flight dispatcher, security department, or anyone responsible for flight safety can quickly and easily see the current risk picture.
Oversight and independence
The CZ&RD is managed by OPSGROUP. Because we are outside the chain of government, we are responsible only to our member airlines and aircraft operators, and more importantly, to the people ensuring a safe flight operation, and to the passengers that fly on our aircraft. For this reason, all information pertinent to a country can be assured to be carried here.
Eternally free
To remain completely independent of any bias, and to ensure that everybody has access, the Conflict Zone & Risk Database is completely free of charge. We have no commercial interest in publishing this information, it exists as a public service because our members care deeply about flight safety.
Contacting us
We rely on your input. If you have information to add, please email report@safeairspace.net. You can also use this address to discuss any content here. The collaborative effort is our focus. We’re still a team of humans, and we miss stuff. If you see something missing here, please tell us!
All submissions are anonymous, and our only concern is for the safety of all airspace users – the crew and the passengers. We appreciate your help.